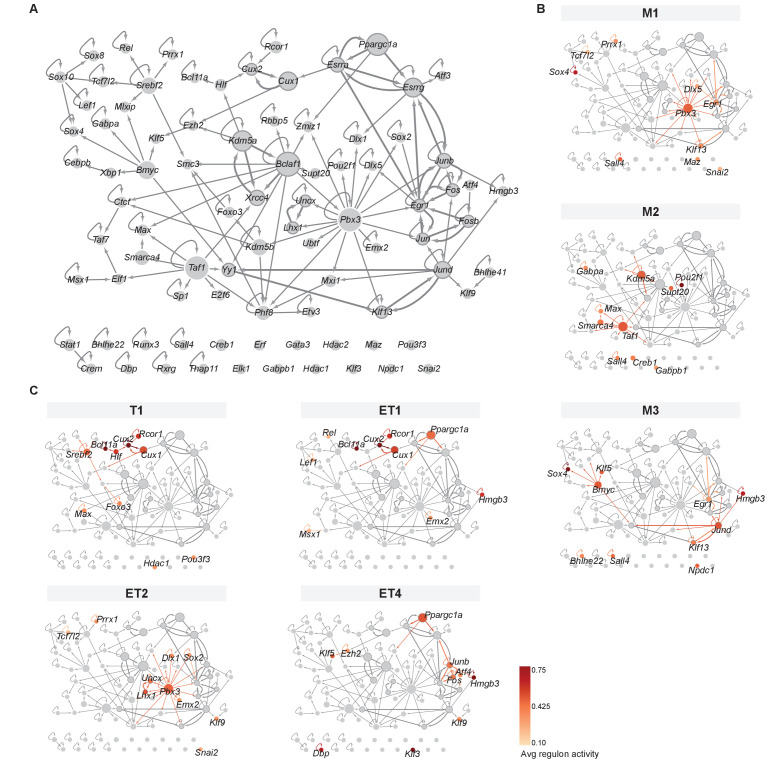
Figure 5. Mitral and tufted cell-specific transcription factor network derived from regulons.
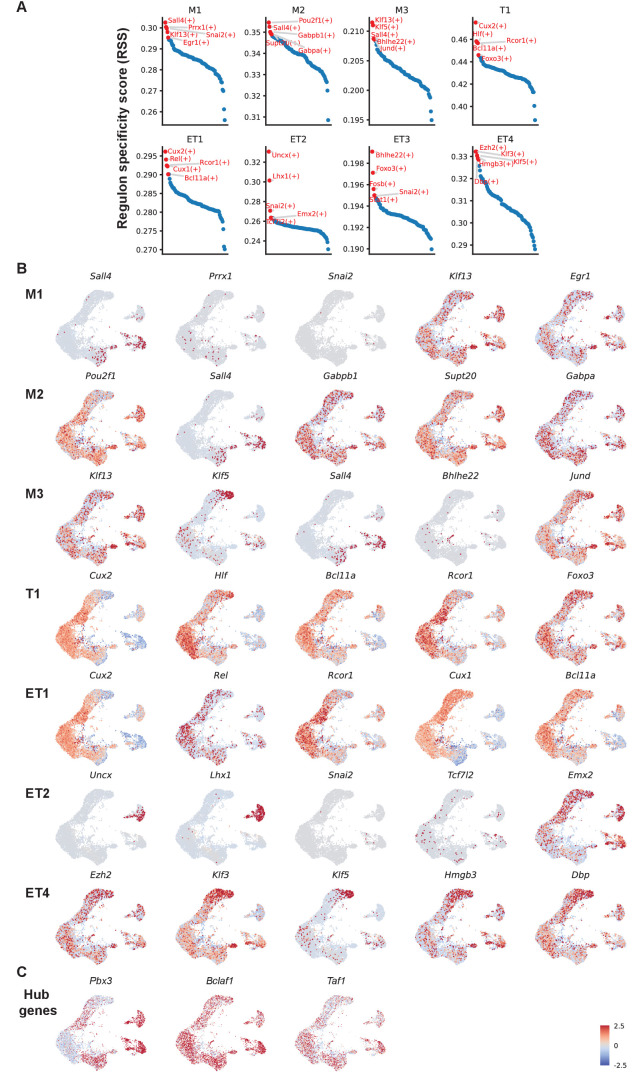
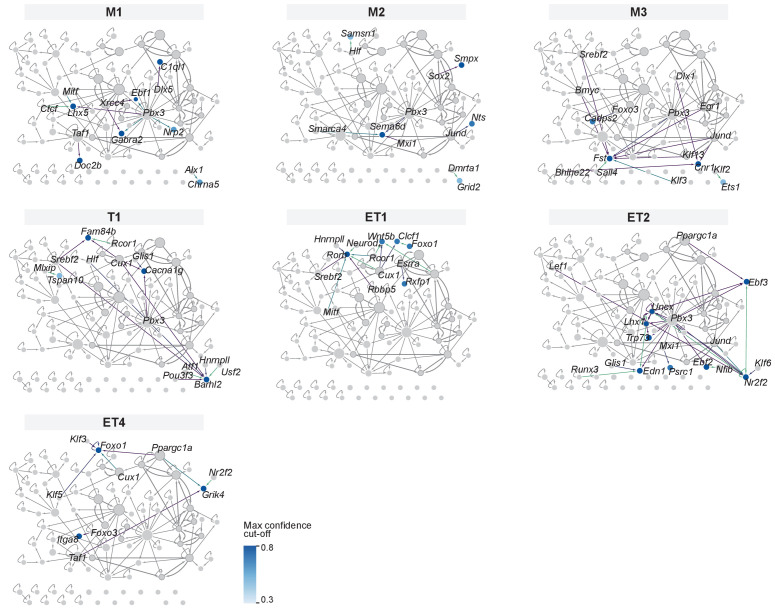
(A) Overview of mitral and tufted cell-specific transcription factor (TF) network, with node size scaled by the number of target genes and nodes colored with different shades of gray based on the outdegree (number of outgoing edges). Thick borders and edges denote cycles of 2 or three regulons. The three main hubs are: Pbx3 (outdegree 17, target genes 545), Bmyc (outdegree 11, target genes 523) and Taf1 (outdegree 9, target genes 551). (B) Same network as shown in A specific for mitral cell types (M1, M2, M3) with standardized regulon activity for the top 10 most specific regulons mapped onto the corresponding TF nodes (compare Figure 4D,E). Regulon specificity scores are shown in Figure 5—figure supplement 1A, with expression of the corresponding TFs visualized on UMAPs in Figure 5—figure supplement 1B. Mitral and tufted cell type-specific marker genes are visualized in the network in Figure 5—figure supplement 2. (C) Same network as shown in (A) specific for tufted cell types (T1, ET1, ET2, ET4) with standardized regulon activity for the top 10 most specific regulons. We omitted ET3 as it only has a few nuclei. As for mitral cell types, see also Figure 5—figure supplements 1 and 2.