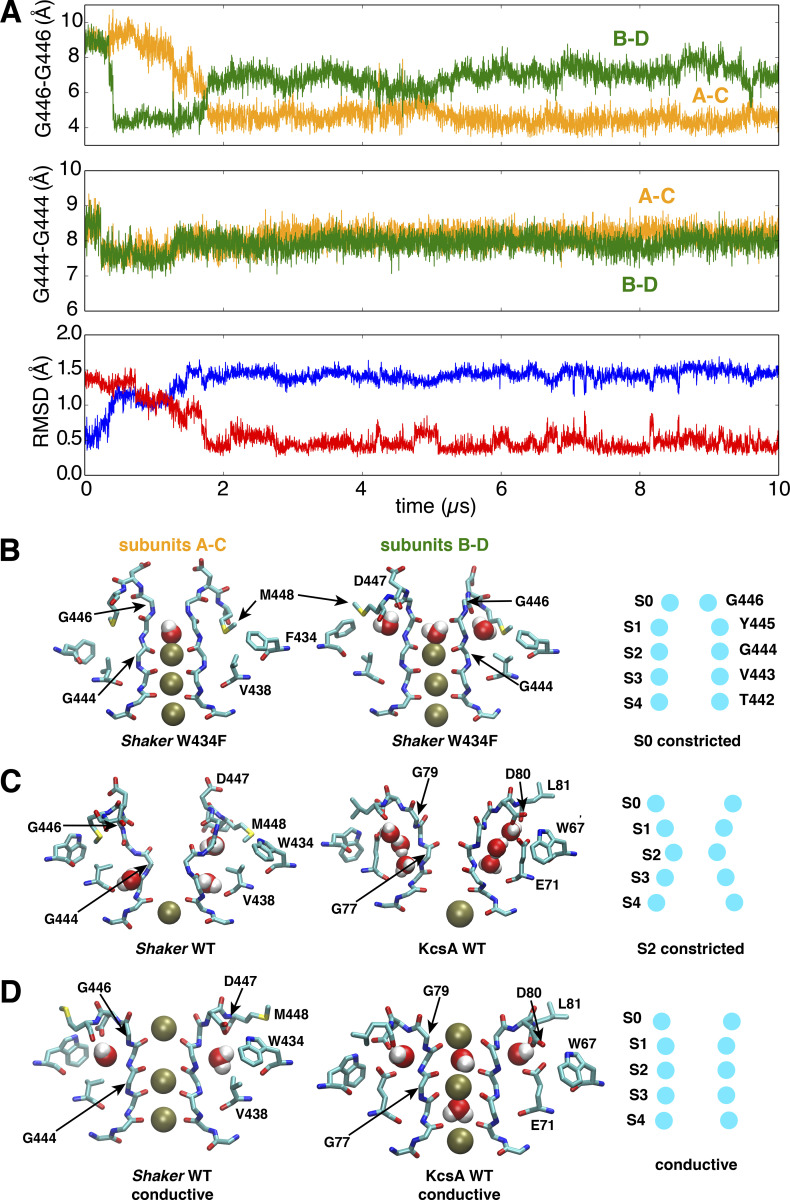
Figure 7.
A stable conformation constricted at the extracellular S0 site of the selectivity filter in a model of the pore domain of the W434F Shaker mutant.(A) Time series of the cross-subunit distance between the Cα atoms of diagonally opposed subunits, respectively, for G446 to monitor the conformation of S0 site (upper) and G444 to monitor the conformation of S2 site (middle), and the RMSD of the selectivity filter backbone (lower) by using the initial (blue) or last (red) conformation as reference. (B) Side views of the last snapshot of the selectivity filter at the end of the 10-µs trajectory for the subunits A and C (left) or B and D (middle) of the W434F Shaker mutant. A scheme (right) is shown to highlight the selectivity filter conformation constricted at the S0 (G446) site. (C) Side views of the selectivity filter for constricted Shaker WT (left) and WT KcsA (middle). Both are constricted at the S2 site as shown in the scheme (right). (D) Side views of the selectivity filter for conductive Shaker WT (left), WT KcsA (middle), and the scheme (right). The simulation of the W434F mutant was performed with a model with an intracellular gate opening of ∼18Å.