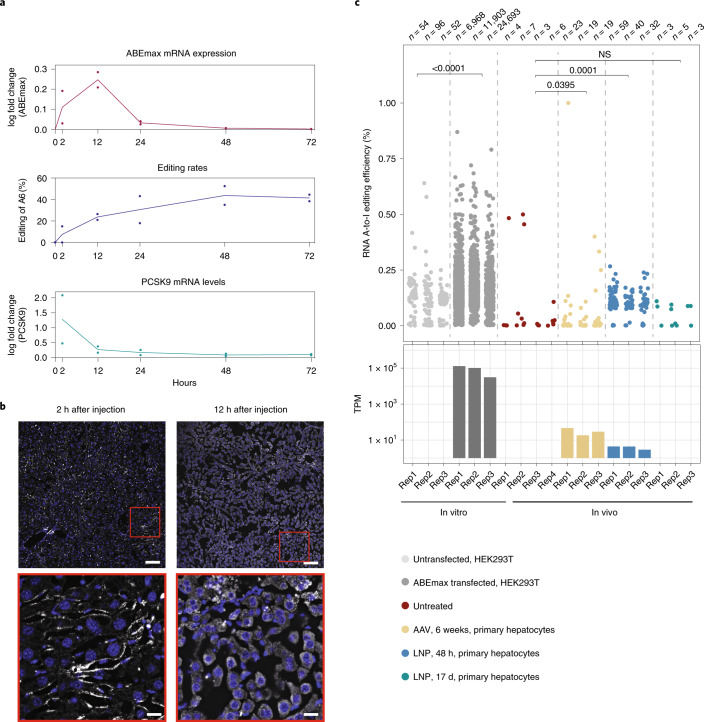
Fig. 2. LNP-mediated ABE mRNA delivery leads to transient base editing without inducing substantial off-target deamination in the transcriptome.
a, LNPs co-formulated with ABE mRNA and sgRNA_mP01 were systemically delivered. The top panel depicts ABEmax mRNA expression assessed by RT–qPCR. The middle panel depicts editing rates assessed by Sanger sequencing. The bottom panel depicts Pcsk9 mRNA levels assessed by RT–qPCR. The line represent mean of n = 2 animals per time point. b, Expression and localization of ABEmax mRNA 2 h or 12 h after injection of 3 mg kg−1 LNP assessed by smFISH in the liver. Twelve hours after injection, mRNA is predominantly cytoplasmatic. Blue, DAPI; white, ABEmax mRNA. Scale bar, top panel, 100 µm; scale bar, bottom panel, 20 µm. smFISH was performed once. c, Top, RNA-wide A-to-I editing assessed by whole-transcriptome sequencing. Each dot represents one editing event. The total number of editing events is indicated above. Each lane represents one individual biological replicate per animal. In vitro RNA-seq data are from HEK293T cells that were co-transfected with plasmids expressing ABEmax and sgRNA_mP01. Means of all replicates per sample were compared using one-tailed unpaired t-test for ex vivo samples and one-way ANOVA for in vivo samples. Bottom, telative TadA transcript expression in transcripts per million (TPM). NS, not significant.