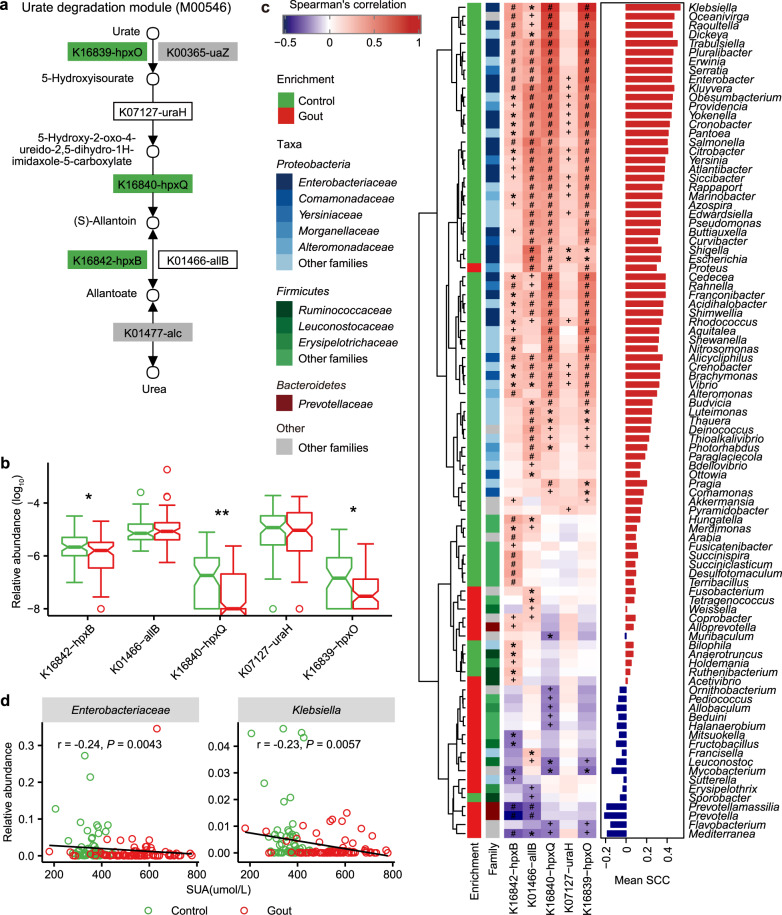
Fig. 2. Gout-associated microbial gene functions related to urate degradation.
a KEGG module for urate degradation. b Relative abundance of KOs involved in urate degradation. Significantly enriched KOs were identified by Wilcoxon rank-sum test, and the boxes or KO names were colored according to the direction of enrichment. Green, enriched in healthy controls (FDR P < 0.05). Boxes with no color or KO names with black, no difference; boxes with gray, not detected in samples. c Correlations between gout-associated genera and urate degradation-associated KOs (red and purple for positive and negative correlation, respectively). Spearman correlation test: ‘plus’ denotes FDR P < 0.05; ‘asterisk’ denotes FDR P < 0.01; ‘hash’ denotes FDR P < 0.001. The enrichment direction and family classification of genera were shown in left panel and the mean Spearman’s correlation coefficient of each genus with urate degradation-associated KOs was shown in the right panel. d The associations between SUA and Enterobacteriaceae or Klebsiella. Spearman’s rank correlation was calculated by taking the species relative abundance and SUA content. An inverse correlation was observed between SUA and Enterobacteriaceae and Klebsiella. For all box and whisker plots, the center line represents median. The bounds of box represent the first and third quartiles. The upper whisker extends from the hinge to the largest value no further than 1.5 * interquartile range (IQR) from the hinge. The lower whisker extends from the hinge to the smallest value at most 1.5 * IQR of the hinge. The notch represents a confidence interval around the median as the median ± 1.58*IQR/sqrt(n). hpxO FAD-dependent urate hydroxylase, uraH 5-hydroxyisourate hydrolase, hpxQ 2-oxo-4-hydroxy-4-carboxy-5-ureidoimidazoline decarboxylase, allB and hpxB allantoinase.