Fig. 3.
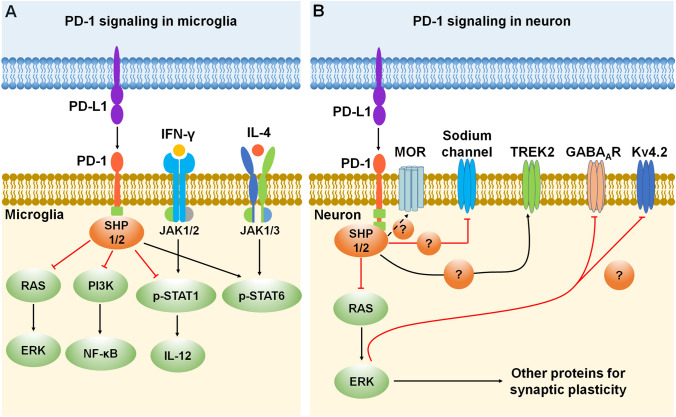
PD-1 signaling and expression in microglia and neurons. A Mechanisms of PD-1 signaling in microglia. PD-1 inhibits microglial function by recruiting phosphatases SHP-1/SHP-2 to the ITIM/ITSM domain in the PD-1 tail and then inhibiting the RAS-ERK and PI3K-NF-κB signaling pathways. Moreover, PD-1 signaling suppresses IFN-γ-activated M1 microglia polarization by reducing the phosphorylation of STAT1 and the secretion of IL-12, while promoting IL-4-activated M2 microglia polarization by increasing STAT6 phosphorylation. B Mechanisms of PD-1 signaling in neurons. Activation of the PD-1 pathway dampens neuronal excitation via activation of the phosphatase SHP-1/2 and resulting in the downstream modulation of sodium and potassium channels (TREK2 and Kv4.2), as well as GABAA receptors. Moreover, PD-1 signaling regulates mu-opioid receptor (MOR) function through activation of the phosphatase SHP-1. Red lines ending in a bar represent inhibitory signaling, and black arrows indicate positive signaling. Abbreviations: PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, PD-1 ligand; SHP, Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase; RAS, a small GTPase encoding RAS (retrovirus-associated DNA sequences); ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PI3K, type I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; p-STAT 1/6, phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 1/6; IL, interleukin; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; JAK, Janus kinase; MOR, mu-opioid receptor; TREK2, TWIK-related K+ channel-2; GABAAR, gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor; Kv4.2, potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 2.