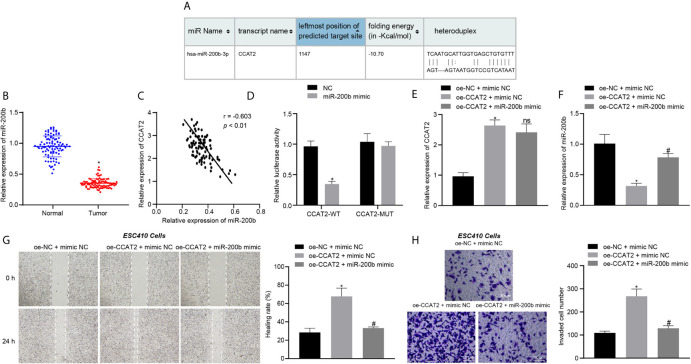
Figure 3.
CCAT2 binds to miR-200b and reduces its expression, thus triggering the proliferation, migration and invasion of ESCC cells. (A) The binding site between CCAT2 and miR-200b predicted by the RNA22 database. (B) RT-qPCR detection of miR-200b expression in 93 cases of ESCC tissues and normal adjacent tissues. (C) Correlation analysis of CCAT2 expression and miR-200b expression in 93 cases of ESCC tissues by Pearson’s correlation analysis. (D) Binding of CCAT2 to miR-200b confirmed by dual luciferase report assay. (E) RT-qPCR detection of the expression of CCAT2 in ESC410 cells after overexpression of CCAT2 and miR-200b. (F) RT-qPCR detection of the expression of miR-200b in ESC410 cells after overexpression of CCAT2 and miR-200b. (G) Scratch assay detection of ESC410 cell migration after overexpression of CCAT2 and miR-200b. (H) Transwell assay detection of ESC410 cell invasion after overexpression of CCAT2 and miR-200b. Scale bar = 50 μm. *p < 0.05 vs. oe-NC + mimic NC-treated cells. # p < 0.05 vs. oe-CCAT2 + mimic NC-treated cells. Data were shown as mean ± standard deviation of three technical replicates. Data between cancer tissues and normal adjacent tissues were compared by paired t-test. Data between remaining two groups were compared by unpaired t-test. Data among multiple groups were compared by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.