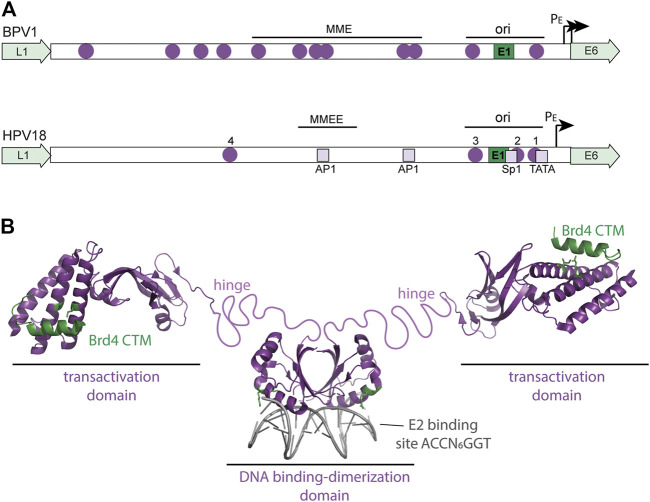
FIGURE 3.
Regulatory elements in the viral URR and structure of the HPV E2 protein. (A) The diagram shows a comparison of the BPV1 and HPV18 Upstream Regulatory Regions (URR). Both URRs contain the replication origin (with E1 and E2 binding sites) as well as the additional E2 sites shown (purple circles). In BPV1, the Minichromosome Maintenance Element (MME) is required for maintenance replication and genome partitioning. In HPV18, a region named the Minichromosome Maintenance Enhancer Element (MMEE) is required for maintenance replication. In HPV18, E2 binding sites #1 and #2 overlap binding sites for Sp1 and TBP (TATA) in the early promoter and thus E2 binding represses transcription. AP1 sites in the URR are important for both transcription and replication of the HPV genome. These cellular binding sites are indicated by light purple squares. Ori: origin of replication; PE: Early Promoter. (B) The structure of the HPV E2-TA protein is shown. The HPV16 transactivation domain is shown bound to the Brd4 CTM peptide (residues 1,343–1,362 in green) from the pdb file 2NNU. The E2 residues important for this interaction (R37 and I73) are shown in green. The dimeric HPV18 DNA binding domain bound to an E2 binding site is from the pdb file 1JJ4. E2 Residues that contact the Brd4 N-terminal regions (R307 and K308) are highlighted in green. An unstructured, flexible linker connects the E2 domains and is named the hinge.