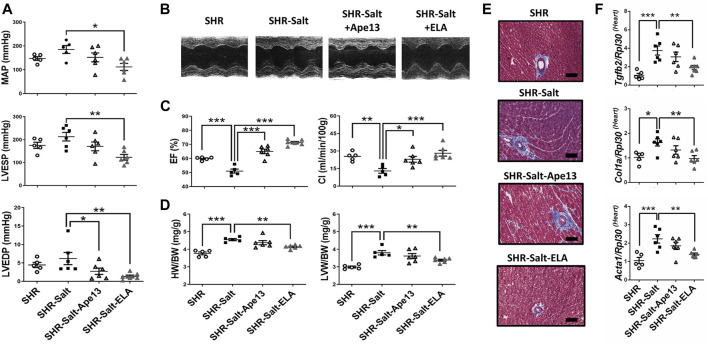
FIGURE 2.
Chronic Elabela infusion alleviates cardiovascular dysfunction and remodeling induced by high-salt diet in hypertensive rats. (A), cardiac function measurements in SHR rats fed with standard-(SHR) or high-salt diet (8% of NaCl) and treated with either Apelin-13 (SHR-Salt-Ape13), Elabela (SHR-Salt-ELA) or saline (SHR-Salt). Mean arterial pressure (MAP), left ventricular end-systolic (LVESP) and end-diastolic pressures (LVEDP) were measured with a pressure catheter; (B), representative images of short axis M-mode echocardiography after 6 weeks of diet regimen; (C), measurement of the ejection fraction (EF%) and cardiac index (CI); (D), heart weight to body weight ratio (HW/BW) and left ventricular weight to body weight ratio (LVW/BW); (E), representative histology of heart stained with Masson’s trichrome (Scale bars: 100 μm); (F), quantitative RT-PCR analysis of pro-fibrosis mRNA levels of transforming growth factor-β2 (Tgfb2), collagen 1a (Col1a), and skeletal muscle α1-actin (Acta1) in hearts. The Ribosomal protein L30 (Rpl30) was used as a reporter gene. Data were normalized to SHR rats fed with standard-salt diet (0.3% of NaCl). (SHR n = 5, SHR-Salt n = 6, SHR-Salt-Ape13 n = 6, and SHR-Salt-ELA n = 6). All data are individual values with means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, the data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post hoc test.