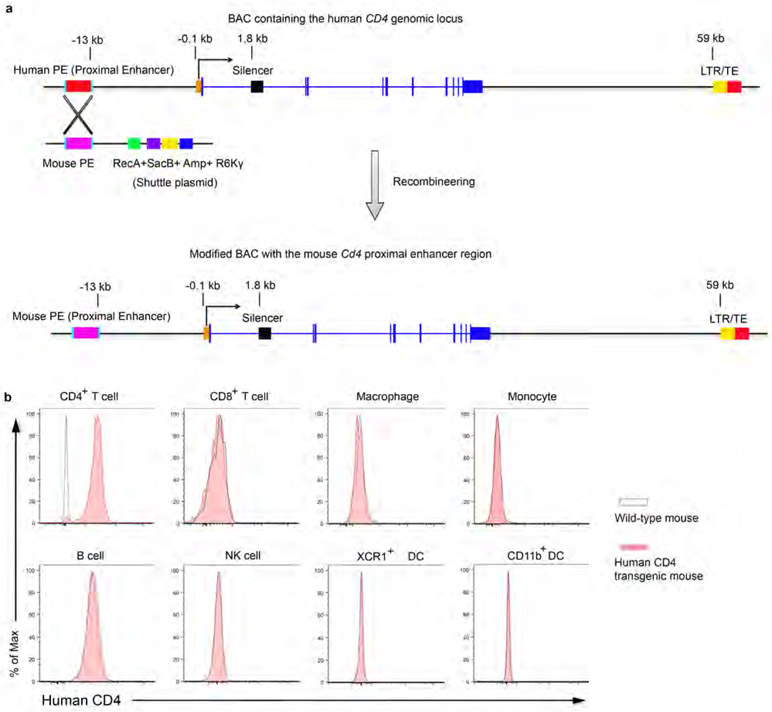
Extended Data Fig. 4 ∣. Generation and validation of human CD4 transgenic mice.
a, Recombineering a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) DNA containing the human CD4 locus with the proximal enhancer (PE) element replaced by its murine equivalent. The shuttle plasmid contains the mouse Cd4 PE flanked by two homologous arms of the human CD4 gene (250 bps), the E coli. RecA gene to mediate homologous recombination, the SacB gene to mediate negative selection on sucrose, an Ampicillin resistance locus to mediate positive selection and a conditional R6Kγ replication origin. b, Flow cytometry analyses of human CD4 expression on leukocyte populations from wild-type or human CD4 transgenic mice. CD4+ T cells (CD45+TCRβ+CD4+), CD8+ T cells (CD45+TCRβ+CD8+), NK cells (CD45+TCRγ−TCRβ−NKp46+NK1.1+) were isolated from lymph nodes. B cells (CD45+MHCII+Ly6C−B220+), XCR1+ dendritic cells (DCs) (CD45+Lin−F4/80−Ly6C−CD11c+MHCII+XCR1+), CD11b+ DCs (CD45+Lin−F4/80−Ly6C−CD11c+MHCII+CD11b+), Monocytes (CD45+Lin−F4/80+Ly6C+CD11b+) and Macrophages (CD45+Lin−F4/80+CD11b−Ly6C−) were isolated from spleens. Data are representative of three independent experiments (b).