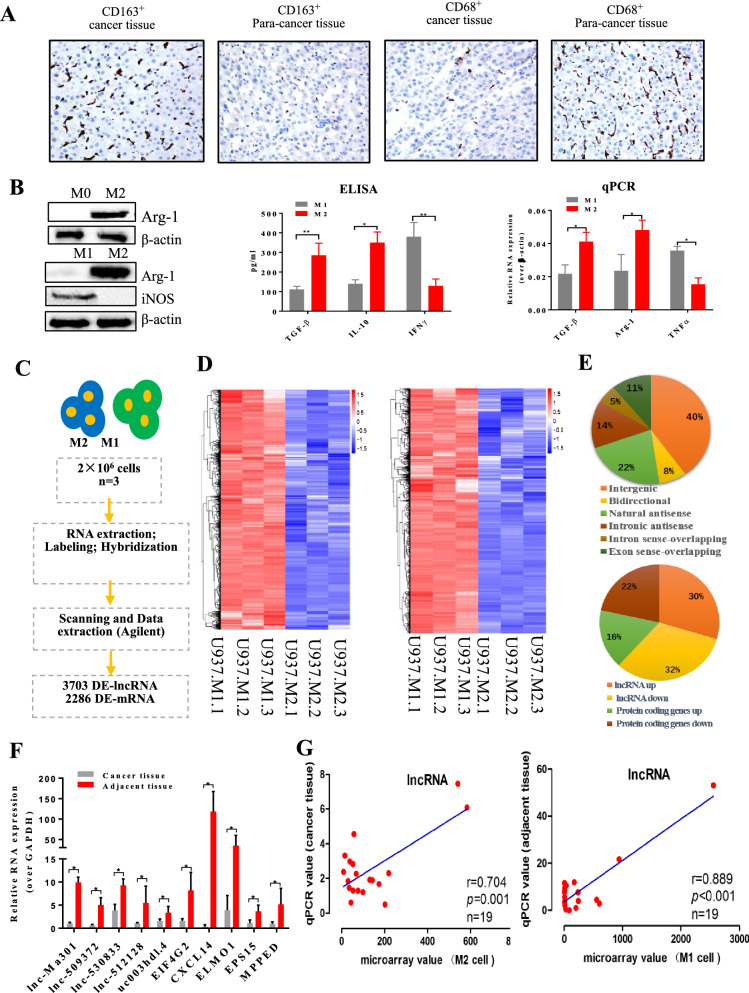
Fig. 1.
Microarray analysis of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and mRNAs during polarization from M2 to M1 macrophages. A CD68 and CD163 immunohistochemical staining in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and corresponding adjacent normal tissues (n = 30). The images represent the distributions of M1 and M2 cells inHCC tissues and adjacent normal tissues. Pictures were taken at 200× magnification. B M2 and M1 phenotype identification. U937 cells gave rise to M2 phenotype macrophages after stimulation with PMA, IL-4, and IL-13, which were polarized into M1 phenotype macrophages by LPS and IFN-γ stimulation. Western blotting, ELISA and qRT-PCR were used to identify the M2 and M1 phenotypes. β-actin was used as a reference for Western blotting. Anti-Arg-1 (40 KD) antibody was used as a marker of the M2 phenotype and iNOS (130 KD) antibody as a marker of the M1 phenotype. TGF-β, IL-10, and IL-12 were also used as markers to identify M2 and M1 macrophages. C Workflow for lncRNA analysis. D Clustering and pairwise comparison of lncRNAs differentially expressed between M1 and M2 cells. E Distribution of six types of lncRNAs as well as down- and up-regulated lncRNAs and mRNAs. F qRT-PCR validation of the selected genes from the microarray data. G Pearson correlation analysis to assess relationships between microarray and qRT-PCR results