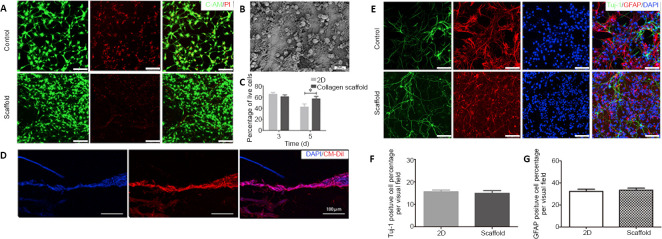
Figure 2.
Biocompatibility of the collagen scaffold with axially-aligned luminal conduits.
(A) Confocal images of C-AM/PI double staining at 5 days. Live cells are labeled green and red signals indicate dead cells. Compared with the control group, NSCs inoculated on the scaffold had a better survival rate. (B) Scanning electron microscopy image of NSCs cultured on the collagen scaffold for 5 days. (C) The quantification of living NSCs. (D) Good growth of CM-Dil-labeled NSCs in the conduit structure of scaffolds. (E) Representative images of immunostaining for Tuj-1 (neurons, Alexa Fluor 488, green) and GFAP (astrocytes, Alexa Fluor 568, red). NSCs inoculated on the scaffolds could differentiate normally as in the control group. (F, G) The quantification of Tuj-1 and GFAP-positive cells in a 200× field. Scale bars: 100 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SD. The experiment was repeated three times. *P < 0.05 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). 2D: Two-dimensional; C-AM: Calcein-AM; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; NSCs: neural stem cells; PI: propidium iodide; Tuj-1: βIII-tubulin.