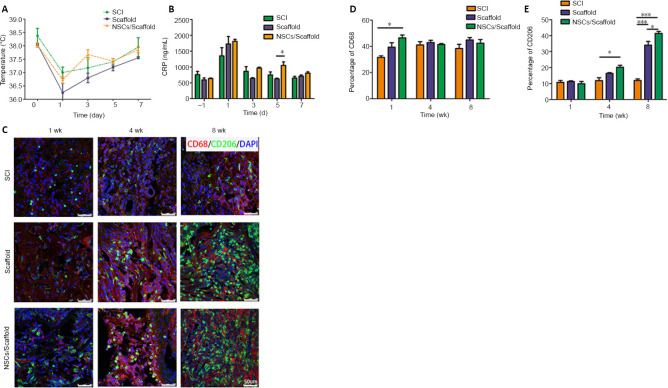
Figure 6.
NSCs/collagen scaffold treatment decreases the inflammatory response in the rat SCI model.
(A) The rectal temperature. (B) CRP levels in the serum. (C) CD68 (Alexa Fluor 568, red) and CD206 (Alexa Fluor 488, green) staining for reactive microglia at 1, 4 and 8 weeks after SCI. The immunogenicity of the scaffolds was low, and the implanted scaffolds did not cause notable inflammation. After 8 weeks, more M2 macrophages infiltrated into the lesion site in the collagen scaffold and NSCs/collagen scaffold groups compared with the SCI group. (D) Quantification of CD68-positive staining in the three groups. (E) Quantification of CD206-positive staining in the three groups. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 16). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). CRP: C-reactive protein; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; NSCs: neural stem cells; SCI: spinal cord injury.