Figure 3.
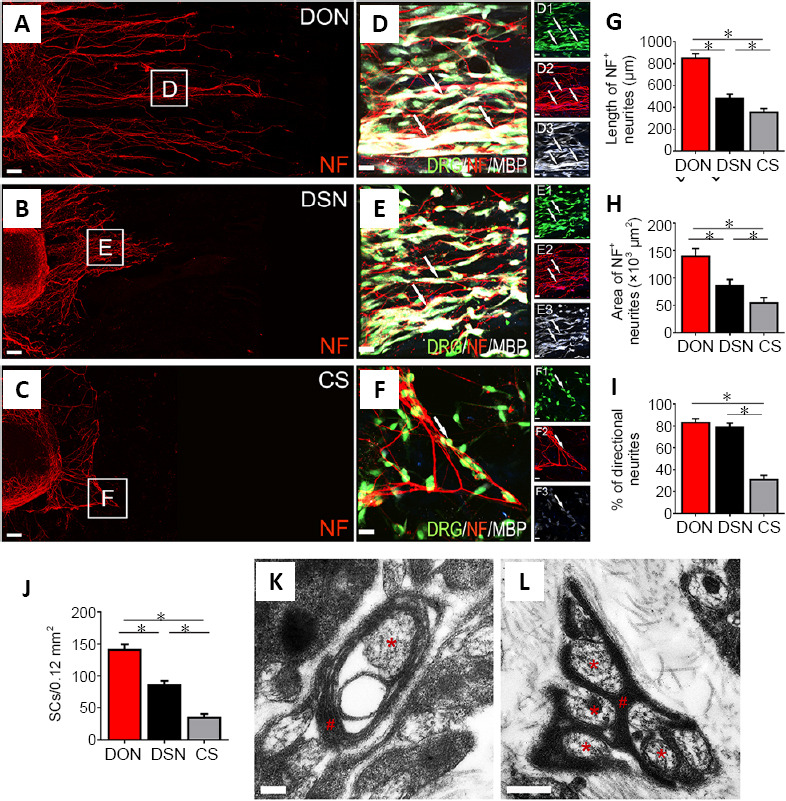
Effects of DON, DSN and CS scaffolds on neurite outgrowth and myelination.
DRGs were seeded on the scaffold slices and cultured for 3 days. (A–C) Showing NF-positive neurite (red) growth on the DON, DSN and CS scaffold slices. (D–F) Enlarged images of the areas in the squares in panels (A–C). NF-positive neurites were adhered by MBP-positive SCs (white) perfectly under the fluorescence microscope (D–F, D1–F3). (G, H) The length and area of neurites on the DON scaffold were the largest, followed by the DSN and then the CS. (I, J) The percentage of directional growth of neurites (I) and number of SCs (J). (K, L) The DON scaffold slice under the transmission electron microscope following 14 days of culture with DRGs in vitro. The neurites (red asterisks) were perfectly wrapped by SCs (red pounds). The data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 5). *P < 0.05 (one-way analysis of variance followed by the least statistical difference test). Scale bars: 100 µm in A–C, 20 µm in D–F, 20 µm in D1–F3, 200 nm in K, 500 nm in L. CS: Collagen sponge; DON: decellularized optic nerve; DRG: dorsal root ganglion; DSN: decellularized sciatic nerve; MBP: myelin basic protein; NF: neurofilament; SCs: Schwann cells.
