Figure 1.
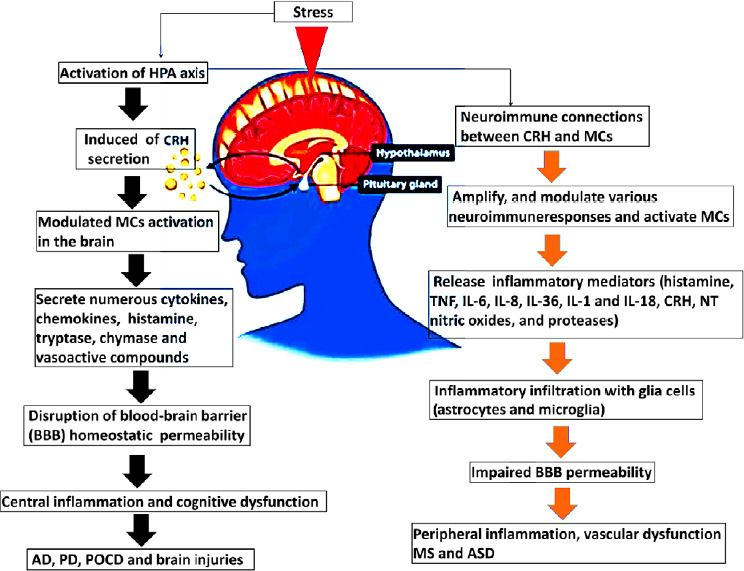
The neuroimmune connections between CRH and MCs associated with central and peripheral inflammation result in neurological disorders.
The schematic diagram shows the effect of stress-induced neuroimmune interactions between CRH and MCs and the link to neurological diseases. Stress conditions activate the HPA axis to induce neuroimmune communication between CRH and MCs to release numerous inflammatory mediators from MCs upon their activation, which in turn disrupts the BBB, leading to neuroinflammatory processes associated with neurological diseases. AD: Alzheimer’s disease; ASD: autism spectrum disorder; BBB: blood–brain barrier; CRH: corticotropin-releasing hormone; HPA: hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal; IL: interleukin; MC: mast cell; MS: multiple sclerosis; NT: neurotensin; PD: Parkinson disease; POCD: postoperative cognitive dysfunction; TNF: tumor necrosis factor.
