Figure 2.
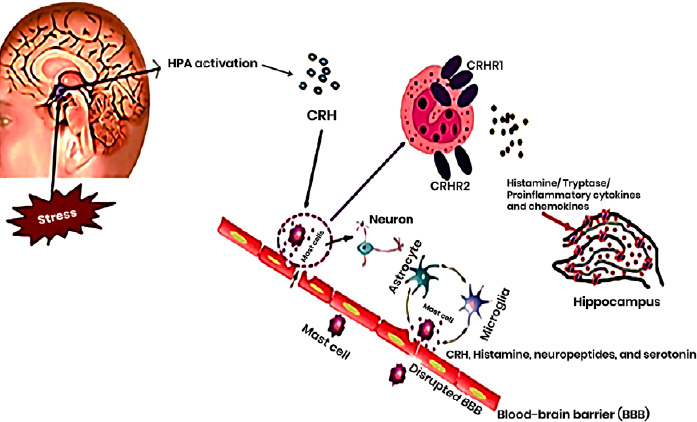
The interactions between CRH and MCs that may affect the BBB under acute and chronic stress.
Acute and chronic stress trigger HPA axis activation to induce the release of CRH, resulting in MC activation and their secretion of histamine, tryptase and proinflammatory cytokines in the hippocampus that affect the BBB and central inflammation. Two CRH receptors are localized on the surface of MCs, and these receptors have different biological effects during stress-induced MC activation. The MCs interact with astrocytes and microglia, which release CRH, histamine, neuropeptides and serotonin, leading to disruption of the BBB. BBB: Blood–brain barrier; CRH: corticotropin-releasing hormone; CRHR: corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor; HPA: hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal; MC: mast cell.
