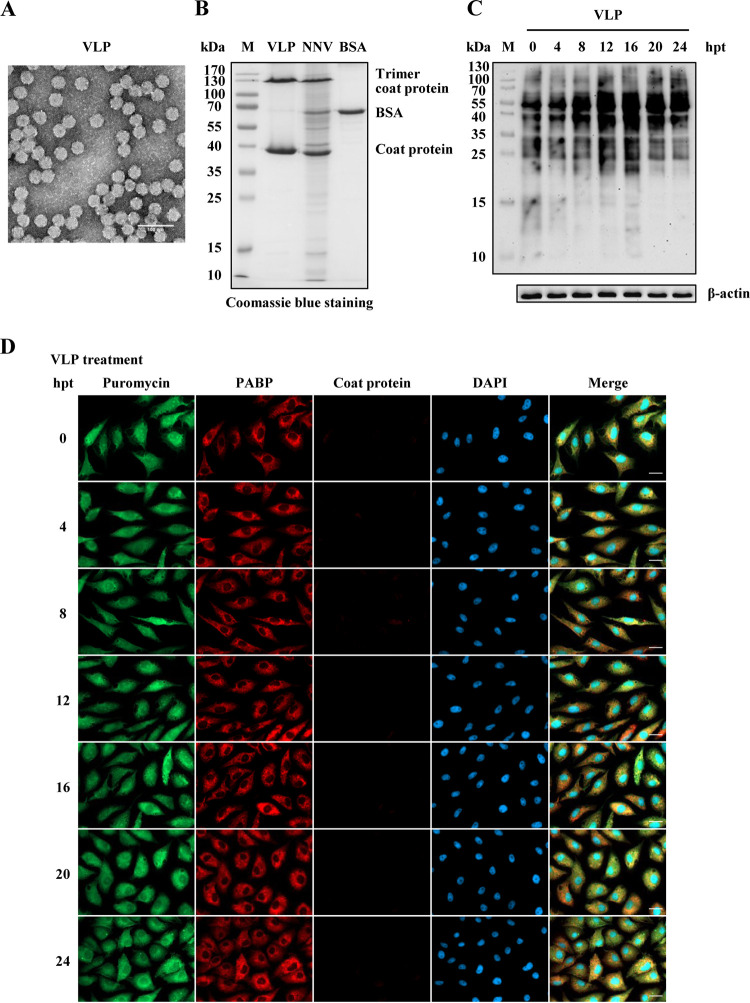
FIG 4.
NNV virus-like particle (VLP) treatment cannot induce GB cell translation shutoff. Recombinant NNV coat proteins prepared as VLPs were used to evaluate the effect on GB cell translation shutoff. (A) Electron micrograph of negatively stained purified NNV VLPs. Bar = 100 nm. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of purified VLPs. BSA (120 ng) was loaded as a quantitative marker. (C) Western blot analysis of newly synthesized protein in VLP-treated GB cells. The amount of VLP protein used to treat GB cells was the same as that present in the NNV infection dose (MOI = 100). Puromycin (20 μg/ml) was added to the medium of treated or untreated cells 1 h before the cells were harvested for Western blotting. A β-actin immunoblot is shown as a loading control. The puromycin incorporated into newly synthesized proteins was detected using an anti-puromycin antibody. (D) Immunocytochemical staining of VLP-treated GB cells. The same VLP treatment as used for Western blotting was used for immunocytochemistry. Newly synthesized proteins with incorporated puromycin were detected using a mouse anti-puromycin Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated monoclonal antibody (green). PABP was detected with a rabbit anti-PABP polyclonal antibody (red). Mouse monoclonal antibody RG-M18 was used to detect GGNNV coat protein (violet). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Bar = 20 μm. BSA, bovine serum albumin; hpt, hours post treatment; M, protein molecular weight marker; PABP, polyadenylate binding protein; VLP, virus-like particle.