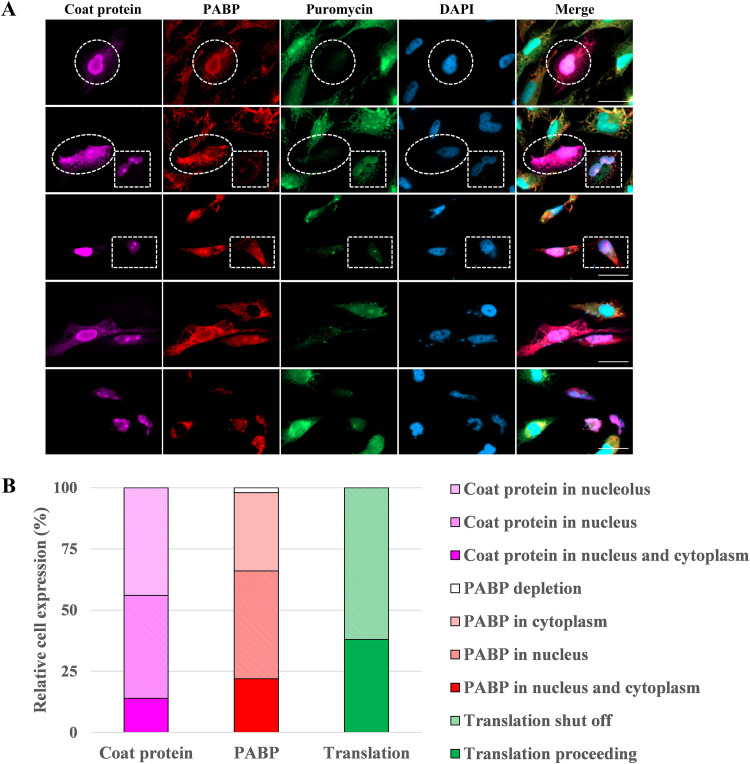
FIG 5.
Ectopic expression of NNV coat protein in GB cells affects PABP and causes host translation shutoff. The effect of overexpressing recombinant NNV coat protein on translation shutoff in GB cells. (A) Immunocytochemical detection of NNV coat protein, PABP, and newly synthesized protein in GB cells that overexpress NNV coat protein. GB cells were transfected with pNNVCP construct (2 μg in a 3-cm tissue culture dish) for 24 h and treated with puromycin 1 h before fixation. Immunofluorescence images of transfected GB cells stained with anti-NNV coat protein antibody (violet), anti-PABP antibody (red), and anti-puromycin antibody-Alexa Fluor 488 (green). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). White circles indicate cells with nuclear colocalization of both NNV coat protein and PABP and with a low level of newly synthesized protein. White ovals indicate cells with nucleus/cytoplasm colocalization of NNV coat protein and PABP and with a low level of newly synthesized protein. White squares indicate cells with nucleolus/nucleus localization of both NNV coat protein and newly synthesized protein and with a low level of PABP. White rectangles indicate cells with nucleolus localization of NNV coat protein, cytoplasm/nucleus localization of PABP and with a low level of newly synthesized protein. Bar = 20 μm. (B) Statistical analysis of the relative cell expression levels in puromycin-labeling (green), PABP expression (red), and NNV coat protein expression (violet) cells of immunocytochemistry. PABP, polyadenylate binding protein. n = 50.