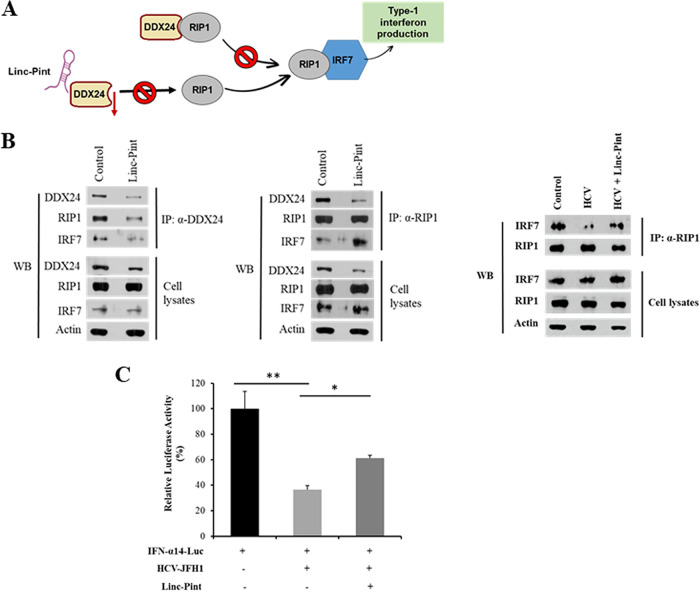
FIG 5.
Linc-Pint induces IFN production by the RIP1-IRF7 pathway. (A) Schematic diagram showing the mechanism of Linc-Pint-mediated IFN signaling. (B) Huh7.5 cells were transfected with the vector control and the pcDNA3 Linc-Pint plasmid. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using DDX24 or RIP1 antibody. The association of DDX24, RIP1, and IRF7 was detected by Western blotting (WB) using specific antibodies. Huh7.5 cells were infected with HCV and transfected with the vector control or the pcDNA3 Linc-Pint plasmid. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using RIP1 antibody. The association of RIP1 and IRF7 was detected by Western blotting using specific antibodies. The cell lysates were also used for Western blot analysis using specific antibodies, and the blot was reprobed with antibody to actin for comparison of protein loads. (C) Huh7.5 cells were mock treated or infected with HCV (JFH1) and then cotransfected with the IFN-α14 luciferase promoter plasmid and vector control or pcDNA3 Linc-Pint plasmid DNA. IFN-α14 promoter activity was measured by a luciferase assay after 48 h of transfection. Data are presented as means ± SD from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was analyzed using two-tailed Student’s t test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.