Figure 6.
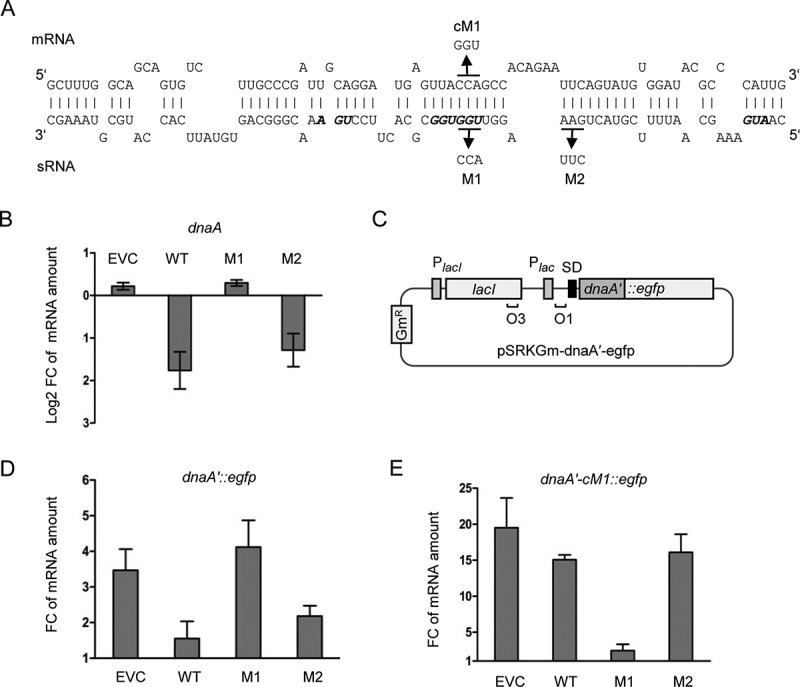
Validation of direct interaction between Ec-rnTrpL and dnaA mRNA in vivo. (A) Scheme of the duplex structure predicted to be formed between dnaA (mRNA) and Ec-rnTrpL (sRNA) (ΔG = −11,74 kcal/mol). The used mutations M1 and M2 in lacZ′-Ec-rnTrpL and the mutation cM1 in dnaA mRNA, which restores the base pairing with the M1-mutation harbouring sRNA, are given. (B) Analysis by qRT-PCR of changes in the dnaA mRNA level 3 min after addition of IPTG to strains containing the empty plasmid pSRKTc (EVC) or its derivatives for induced production of the wild-type, recombinant sRNA lacZ′-Ec-rnTrpL (WT; see Fig. 4B) or mutated sRNAs harbouring one of the indicated mutations (see panel A). (C) Schematic representation of the plasmid used for IPTG-inducible transcription of the dnaA′::egfp reporter fusion. For other details, see Fig. 4B and Fig. 2B. (D) Analysis by qRT-PCR of changes in the dnaA′::egfp mRNA level 3 min after addition of IPTG cultures harbouring pSRKTc (EVC) or its derivatives for induced production of WT or mutants sRNAs (see panel B). (E) Analysis by qRT-PCR of changes in the dnaA′-cM1::egfp mRNA level 3 min after addition of IPTG cultures harbouring pSRKTc (EVC) or its derivatives for induced production of WT or mutants sRNAs (see panel B). The rpoB gene was used as a reference. Cultures grown in LB medium were used. Each graph shows means and standard deviations from three independent experiments
