Figure 8.
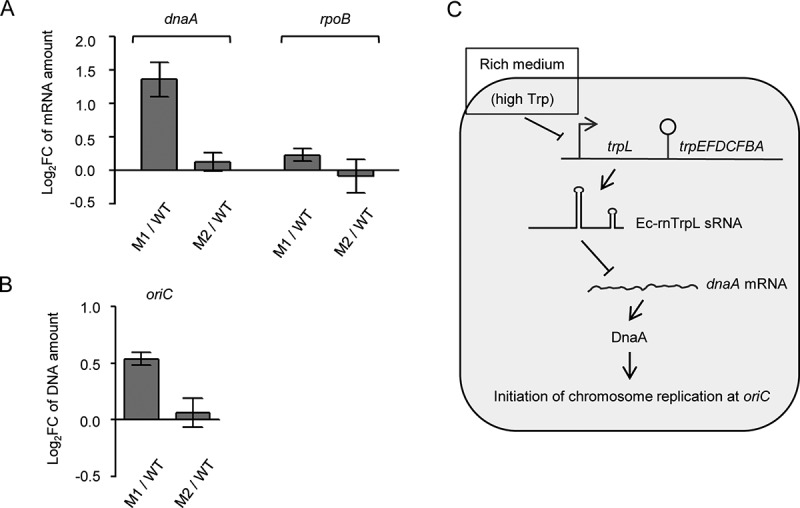
Chromosomal mutations in Ec-rnTrpL confirm function in regulation of dnaA and replication initiation. (A) The relative amounts of dnaA mRNA were analysed by qRT-PCR. The level in strains carrying the M1 or M2 mutations (see Fig. 6A above) was compared to the level in the wild type. The rpoB mRNA was analysed as a non-target RNA. A spike-in transcript was used as reference. (B) The oriC level was analysed by qPCR. The level in strains carrying the M1 or M2 mutations was compared to the level in the wild type. As a reference, terC was used. Cultures grown in minimal medium to the OD of 0.3 were used. Shown are means and standard deviations from three independent experiments. (C) Model for posttranscriptional regulation of dnaA expression and initiation of chromosome replication by Ec-rnTrpL. In rich medium, the high Trp supply leads to repression of Ec-rnTrpL transcription. Since Ec-rnTrpL binds to dnaA mRNA and downregulates its level, in rich medium the dnaA expression is activated at the level of RNA, leading to more frequent initiation of chromosome replication
