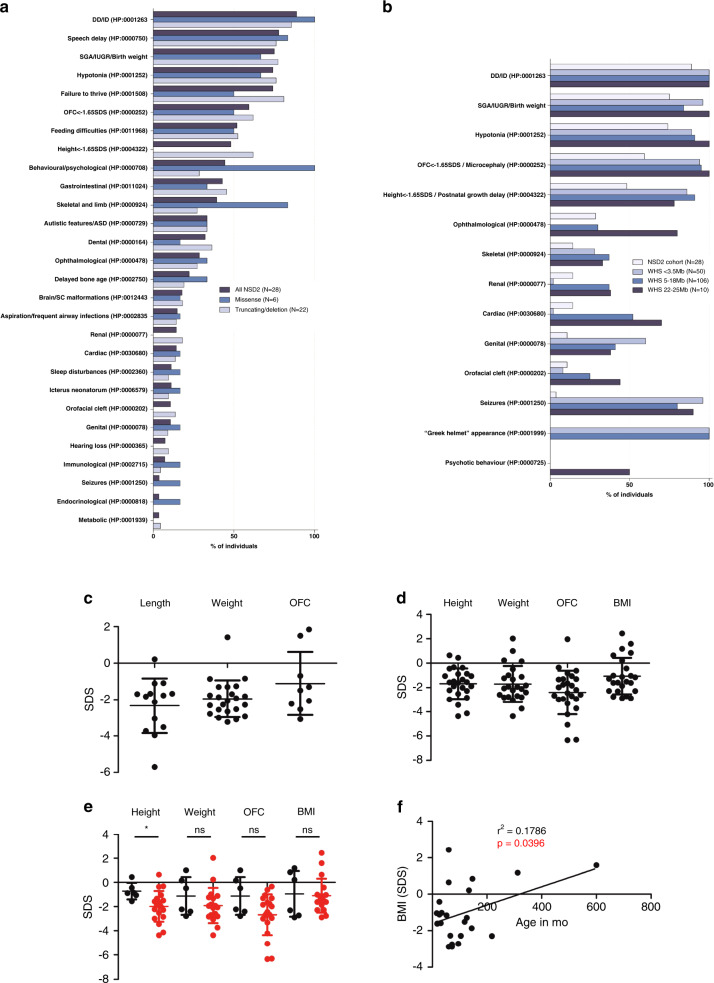
Fig. 3. Phenotypic features and growth parameters of the individuals carrying NSD2 pathogenic variants and comparison with Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome (WHS).
The diagram in (a) summarizes the phenotypic features of the individuals described in this study (18 additional patients together with 10 previously reported individuals) based on the type of NSD2 variant carried. In (b) all individuals are compared with WHS patients, subdivided according to the size of the 4p deletion carried, as reported in Zollino et al.3 Data in (a) and (b) are expressed as percentages. Growth parameters at birth (c; included the parameters at termination of pregnancy for individual 16-I) and at last visit (d) are reported. The average measures for all combined individuals standard deviation score (SDS [SD]) were length (L): -2.3 (1.5); weight (W): -2.0(1.0); occipitofrontal circumference (OFC): -1.1(1.7); gestational weeks (GW): 38.5(3.8) at birth and height (H): -1.7(1.3); W: -1.7(1.5); OFC: -2.4(1.8); body mass index (BMI): -1(1.5) at last visit. (e) Comparison of the growth parameters at last visit for patients carrying missense variants (black) compared with patients carrying other variants as well as deletions encompassing NSD2 (red). *p value < 0.05 as tested by two-tailed Student’s t-test. The data in (c–e) are expressed as SDS based on the respective growth charts. Lines and whiskers represent mean ± SD. (f) Linear correlation analysis between age and BMI and last visit. ASD DD/ID developmental delay/intellectual disability, IUGR intrauterine growth restriction, SC spinal cord, SGA small for gestational age.