Figure 7: β-AR signaling impairs TCR signaling.
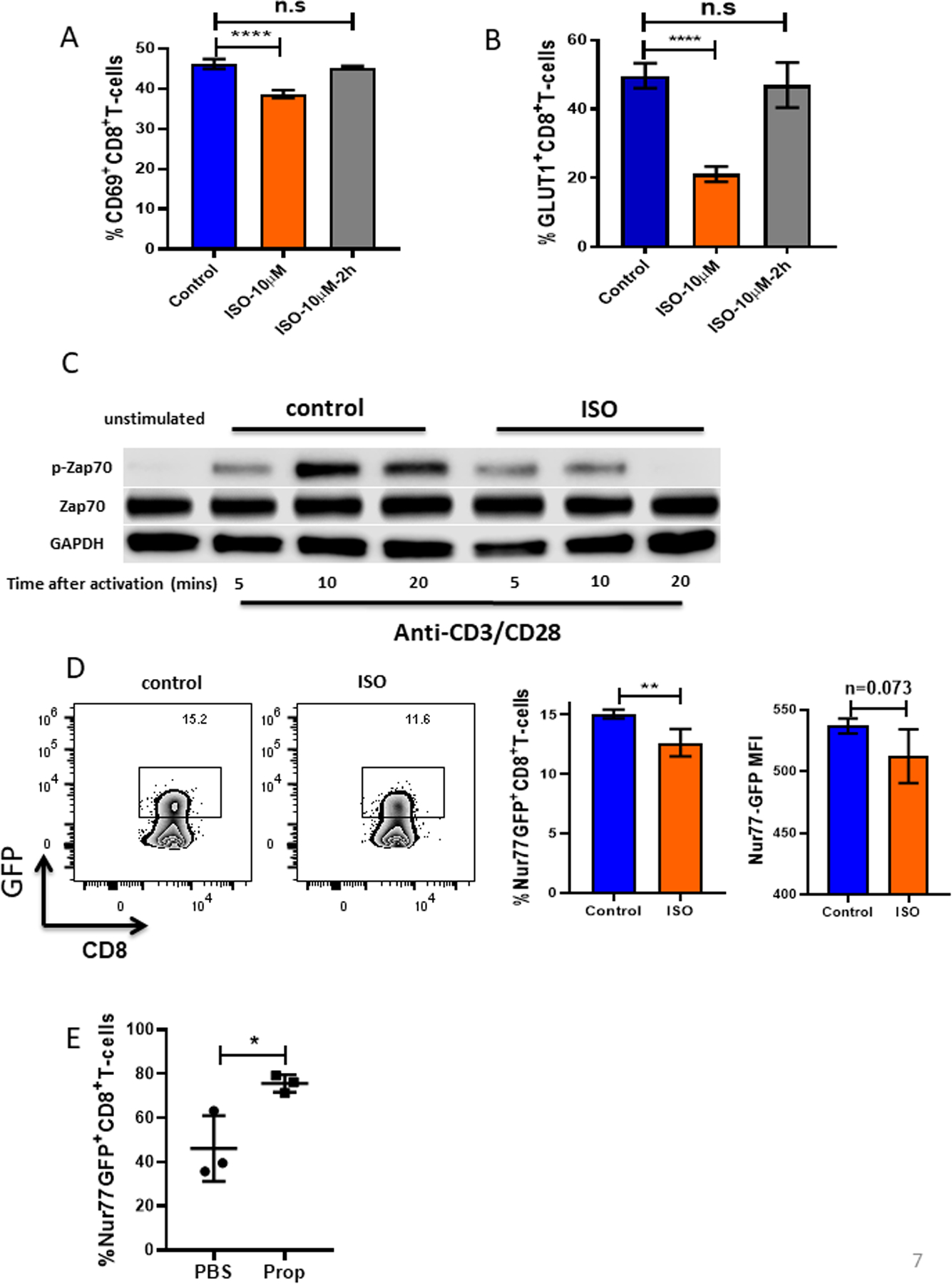
(A-B) CD8+ T cells from BALB/c mice were isolated and purified from lymph nodes and spleens of non-tumor-bearing mice, activated with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies, and treated with or without isoproterenol (ISO, 10μM). (A) CD69 and (B) GLUT-1 were measured by flow cytometry 24 hours after activation. (C) CD8+ T cells activated and treated with or without ISO were collected and lysed. Total ZAP-70, phosphorylated ZAP-70, and GAPDH protein expression were assessed by Western blot at the indicated times. (D) CD8+ T cells from Nur77-GFP reporter mice were isolated and purified from lymph nodes and spleens of non-tumor-bearing mice and activated with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies with or without ISO. Nur77, represented by GFP, was measured by flow cytometry 4 hours after activation. MFI: mean fluorescence intensity. (E) 2×105 B16-OVA cells were injected into C57BL/6 mice. Mice were treated daily with either PBS or propranolol (Prop, 200ug) starting 5 days before tumor implantation and continuing through the end of experiment. Single-cell suspensions were made from B16-OVA tumors. Nur77 was represented by GFP and was measured by flow cytometry. n = 3/group; data are presented as mean±SD; one of two independent experiments. Data were analyzed using Student’s t-test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001.
