FIGURE 3. Effect of Sca-1+ LMSCs and neutrophils on the growth of K pneumoniae.
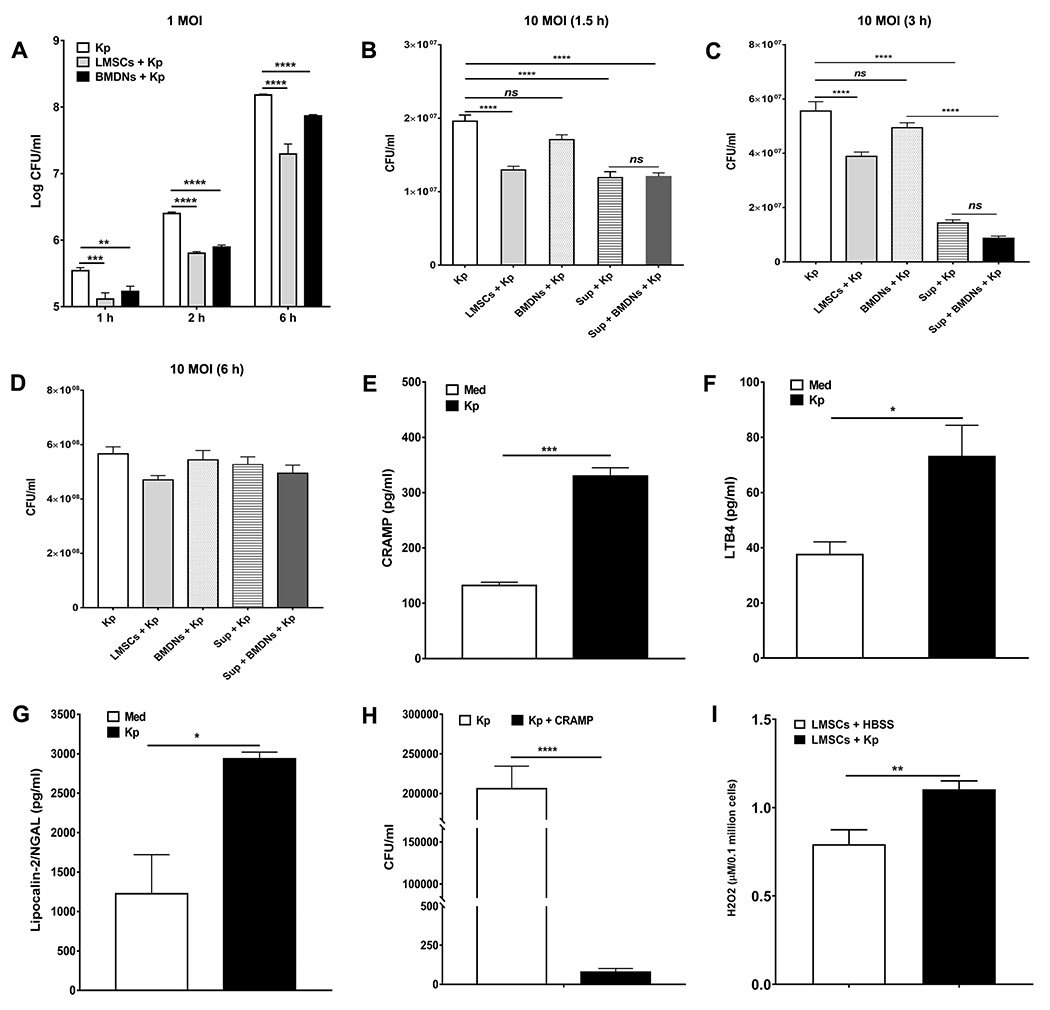
Both Sca-1+ LMSCs and BMDNs showed similar killing effects at all time points tested when infected with low MOI (1 MOI) of K. pneumoniae (A). **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001 for the indicated comparisons. Data are mean ± SEM from three separate experiments (quadruplicate samples). Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Turkeys multiple comparisons test at each time point. However, the killing effects of Sca-1+ LMSCs and LMSC-derived supernatants were remarkably higher at 1.5 h (B) and 3 h (C) post-infection than that of BMDNs when infected with a higher MOI (10 MOI) of K. pneumoniae. Both Sca-1+ LMSCs and their supernatants as well as BMDNs failed to inhibit the growth of K. pneumoniae (10 MOI) at 6 h post-infection (D). Results are the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. ****, p < 0.0001 for the indicated comparisons. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Infection with K. pneumoniae induces the secretion of CRAMP (E), LBT4 (F) and lipocalin-2/NGAL (G) in Sca-1+ LMSCs. Results are the mean ± SEM of triplicate samples from each group. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001 by unpaired t test. (H) CRAMP is potent for killing K. pneumoniae in vitro. Results are the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Each experimental condition was carried out using triplicate samples. ****, p < 0.0001 for the indicated comparison. Data were analyzed using unpaired t test. (I) LMSCs secrete H2O2 following infection with K. pneumonia. Results are the mean ± SEM from three separate experiments. **, p < 0.01 for the indicated comparison. Data were analyzed using unpaired t test.
