FIGURE 5. Effect of Sca1+ LMSCs on K. pneumoniae-induced inflammation.
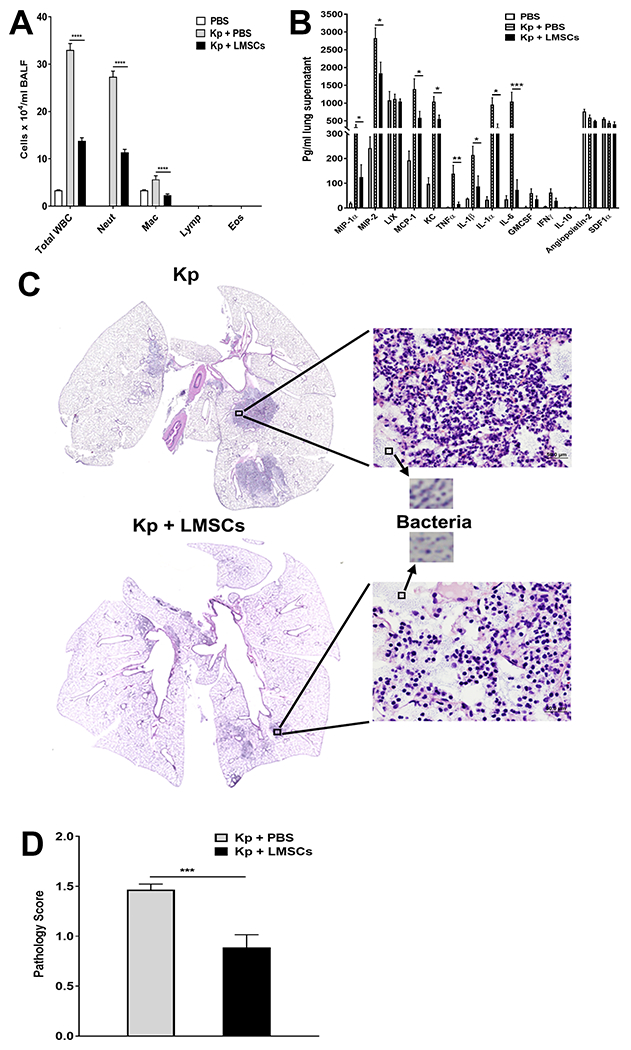
(A) K. pneumoniae-infected mice treated with Sca-1+ LMSCs show reduced total white blood cells and predominantly reduced levels of neutrophils and macrophages in the BALF when compared to K. pneumoniae-infected and PBS-treated mice. Data are mean ± SEM from three independent experiments (n = 5 - 6 mice/group). ****, p < 0.0001 for the indicated comparisons. Data (for each inflammatory cell type) were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. WBC, white blood cells; Neut, neutrophils; Mac, macrophages; Lymph, lymphocytes; Eos, eosinophils. (B) Analysis of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors in the lung supernatants using the Millipore magnetic bead assay. Data are mean ± SEM of 5=6 mice/group. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 for the indicated comparisons. Data were analyzed using multiple t tests. (C) Treatment with Sca-1+ LMSCs reduced K. pneumoniae-induced pathologic lesions in the lungs of mice. Representative photomicrographs of H&E-stained lung sections (magnification, x40) from K. pneumoniae-infected (top left panel)/K. pneumoniae-infected and Sca-1+ LMSC-treated mice are shown (bottom left panel). Magnified images (x200) show the presence of inflammatory cells (top and bottom right panels) and granular microcolonies of bacteria (indicated by arrows) in the lungs of K. pneumoniae-infected/K. pneumoniae-infected and Sca-1+ LMSC-treated mice. D) Lung injury scores. Data are mean ± SEM from two independent experiments (n = 5-6 mice/group). ***, p < 0.001. Data were analyzed using unpaired t test.
