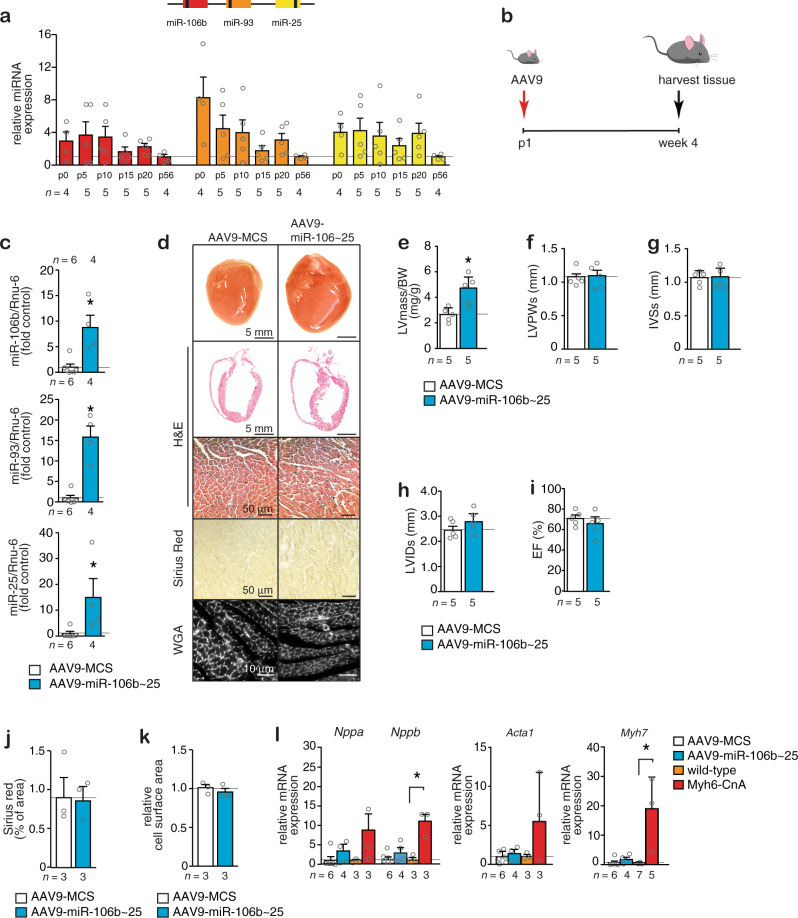
Fig. 2. Overexpression of the miR-106b~25 cluster induces cardiac growth with sustained function.
a Real-time PCR analysis of miR-106b, miR-93, and miR-25 abundance in mouse hearts at postnatal day 0 (p0), p5, p10, p15, p20, and p56 (2 months) of age. b Design of the study. c Real-time PCR analysis of miR-106b, miR-93, and miR-25 abundance in AAV9-MCS versus AAV9-miR-106b~25 hearts, 4 weeks after injection. d Representative images of whole hearts (top panels), H&E-stained sections of four-chamber view (second panel), high magnification H&E sections (third panel), Sirius Red stained sections (fourth panel), and WGA-stained (fifth panel) sections. Quantification of e LV/BW ratio, f LVPWs, g IVSs, h LVIDs, and i EF of mice that received AAV9-MCS or AAV9-miR-106b~25. Quantification of j the fibrotic area by Sirius Red staining and k the cell surface areas by WGA-staining. l Real-time PCR analysis of Nppa, Nppb, Acta1, and Myh7 in hearts from mice that received AAV9-MCS or AAV9-miR-106b~25; or WT or calcineurin transgenic (Myh6-CnA) mice, a mouse model for heart failure, n refers to number of animals. *P < 0.05 vs corresponding control group (error bars are s.e.m.). Statistical analysis consisted of a two-tailed Student’s t-test (c, e–k) or a One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett multiple comparison test (l). Source data are provided as a Source data file.