Figure 3. PFKFB3 is required for fascin to promote glycolysis.
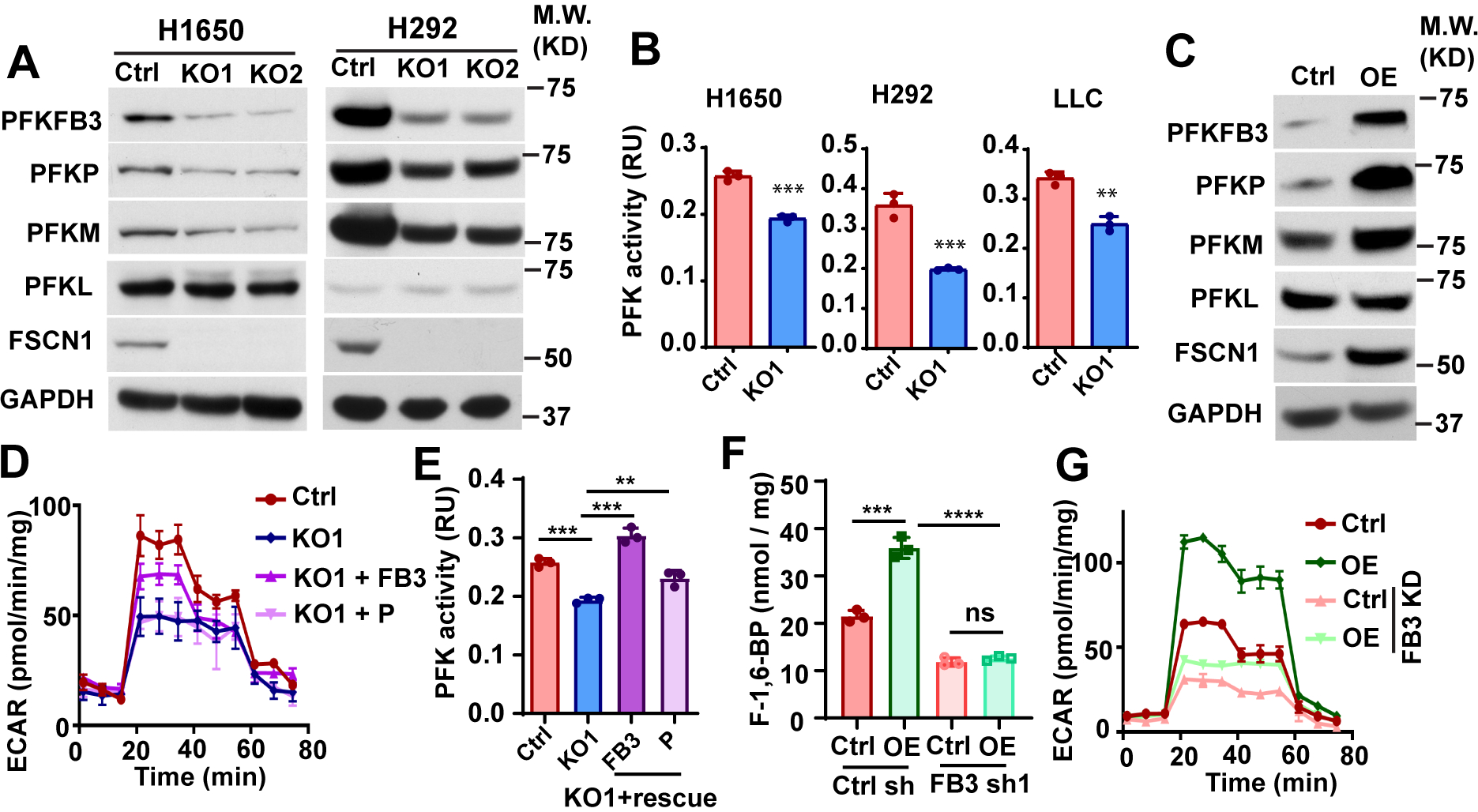
A and B, the effects of fascin KO on PFK protein expression levels (A) and PFK activities in NSCLC cells.
C, the effect of fascin overexpression (OE) on PFK protein levels in H1650 cells.
D, PFKFB3 or PFKP were ectopically expressed in fascin KO H1650 cells and the effect of ectopic PFKs on ECAR was determined. The ectopic expression of PFKFB3, but not PFKP could partially rescue ECAR in fascin KO cells.
E and F, the effect of ectopic PFKFB3 (FB3) or PFKP (P) on PFK activities (E) and F-1,6-BP levels in fascin KO H1650 cells.
G, the effects of PFKFB3 knockdown (FB3 KD) on ECAR in H1650 cells stably expressing control vector (Ctrl) or wild type fascin (OE).
Data in B, E and F were analyzed by two-tailed, two-sample unpaired Student’s test. Representative results from at least three independent experiments are shown. **, *** and **** indicated p<0.01, 0.001 and 0.0001, respectively. ns, not significant.
