Fig. 3: Lung cell types and organoids.
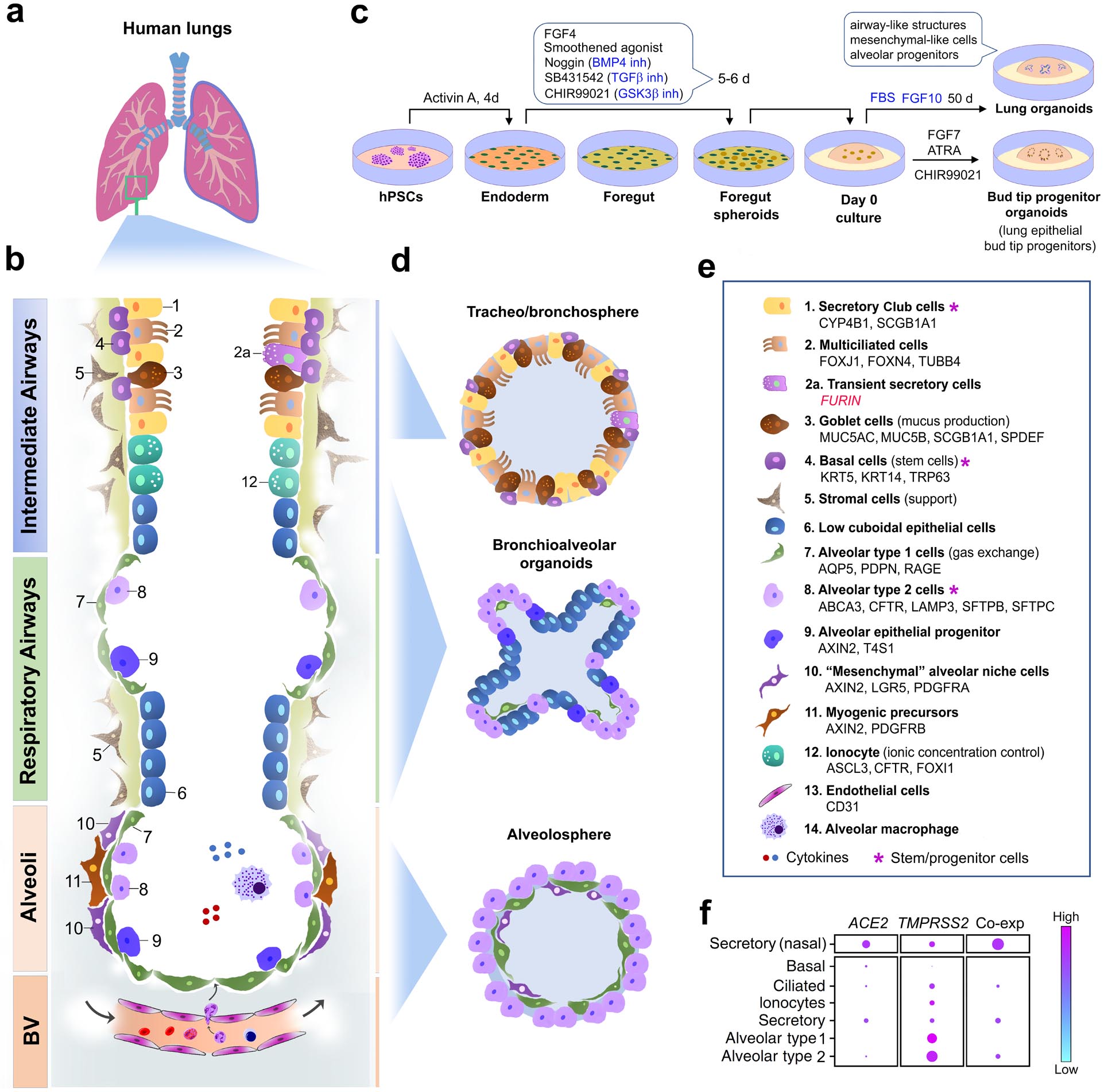
(a) Human lung anatomy. (b) Schematic of the major cell types in different compartments of the human lung, partially adapted from references78,97–99. (c) A representative protocol for the generation of lung organoids containing cell types of interest107. (d) Schematic of lung organoids that model different cellular compartments of the lung. (e) Cell types in panels b and d, with gene and protein markers listed alphabetically78,97–99,163,164. (f) Representative single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of CoV-2 receptor gene expression and co-expression (co-exp)109 in major cell types of the respiratory airways and alveoli. Nasal secretory cells are used as control for comparison. The size of the dots is proportional to the percentage of cells that express indicated genes (adapted from the published data in reference109).
Abbreviations: ABCA3, ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member 3; ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; AQP5, aquaporin 5; ASCL3, Achaete-Scute family BHLH transcription factor 3; ATRA, all-trans retinoic acid; BMP4, bone morphogenetic protein 4; BV, blood vessels; CFTR, CF transmembrane conductance regulator; CYP4B1, cytochrome P450 family 4 subfamily B member 1; d, day(s); FBS, foetal bovine serum; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FOXI1, forkhead box I1; FOXJ1, forkhead box J1; FOXN4, forkhead box N4; GSKβ, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; hiPSC, human induced pluripotent stem cells; inh, inhibitor; KRT5/14, keratin 5/14; LAMP3, lysosomal associated membrane protein 3; LGR5, leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5; PDGFRA/B, platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha/beta; PDPN, podoplanin; SCGB1A1, secretoglobin family 1A member 1; SFTPB/C, surfactant protein B/C; SPDEF, SAM pointed domain containing ETS transcription factor; TMPRSS2, transmembrane serine protease 2; TUBB4, tubulin beta 4B class IVb.
