Fig. 1. Domain structure of human AR and its subcellular mobilization.
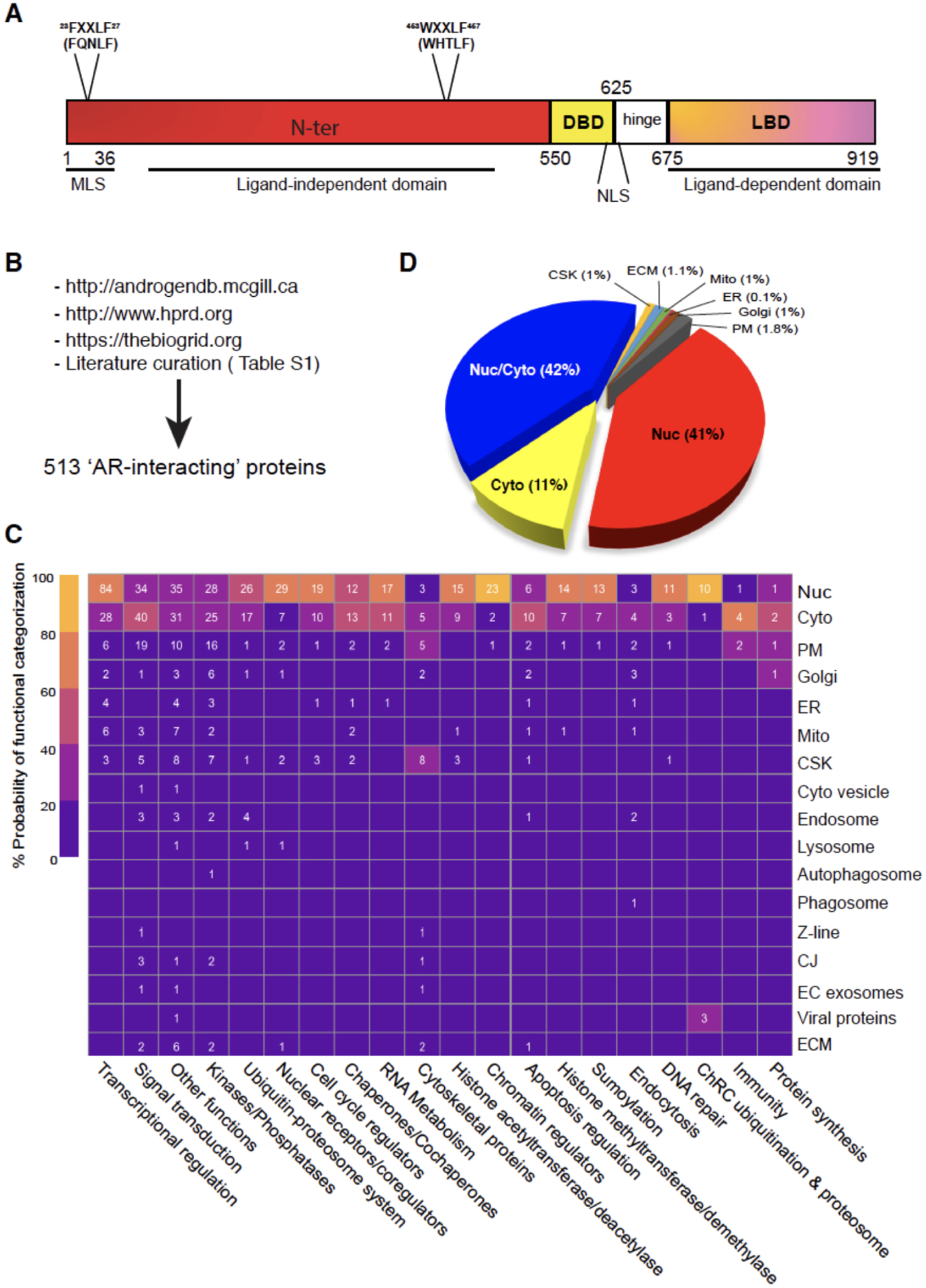
(A) The protein domain structure of human AR. AR is a protein of 919 amino acids (aa) consisting of several functional domains including N-terminal domain (NTD), DNA binding domain (DBD) and ligand binding domain (LBD) at the C-terminus. Also depicted are the FXXLF motif at aa 23–27, the WXXLF motif at aa 453–457, the nuclear localization signal (NLS) and a putative mitochondrial localization signal (MLS).
(B) Pipelines and methods used to curate putative AR-interacting proteins. A total of 513 AR-interacting partners were identified using McGill/HPRAD/Bio-Grid databases as well as extensive literature search and curation (also see Table S1). Note that the AR-interacting proteins encompass those that physically interact with AR (either directly with AR or indirectly through other proteins) as well as those that functionally interact and interface with AR (signaling) but without any physical interactions.
(C) Categorization of AR-interacting partners via their functions and subcellular localizations. The heatmap, generated using Morpheus (a Broad Institute’s web-based heatmap builder), presents the 513 AR-interacting proteins according to their potential involvement in the indicated biological processes (x-axis) and subcellular localizations (y-axis). The heatmap legend indicates the relative probability (%) of AR-interacting partners of falling into a specific functional category. For instance, the upper left box with 84 indicates that 84 AR-interacting proteins in the nucleus function, with 60–80% probability (certainty), in ‘Transcriptional regulation’. On the other hand, the upper right box with 1 indicates that 1 AR-interacting protein in the nucleus functions, with 20–40% probability, in ‘Protein synthesis’. Nuc (nucleus), Cyto (cytosol), PM (Plasma membrane), Golgi (Golgi apparatus), ER (endoplasmic reticulum), Mito (mitochondria), CSK (cytoskeleton), Z-line (the dark band in each myofibril where actin and myosin filaments overlap), CJ (cell junction), EC (extracellular), ECM (extracellular matrix).
(D) Pie chart (%) presentation of the 513 AR-interacting proteins according to their subcellular localizations.
