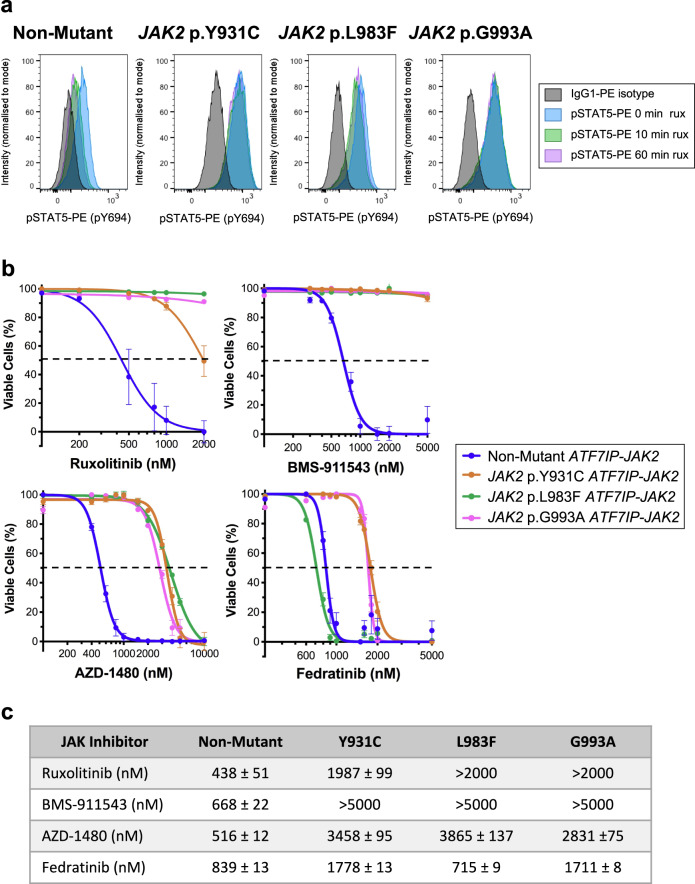
Fig. 2. ATF7IP-JAK2 Ba/F3 cells with acquired mutations are resistant to multiple type-I JAK inhibitors.
a Non-mutant or RuxR-mutant (JAK2 p.Y931C, p.L983F, or p.G993A) ATF7IP-JAK2 expressing Ba/F3 cells were incubated in 50 nM rux for up to 1 h. At 0, 10, and 60 min timepoints, STAT5 p.Y694 phosphorylation was assessed by intracellular flow cytometry in comparison to cells stained with an IgG1-PE isotype control antibody (black). Channel intensity was normalized to the percentage of maximum count and pSTAT5-PE mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs) are shown. Histograms are representative of three independent experiments. b Ba/F3 cells expressing either non-mutant or RuxR-mutant (JAK2 p.Y931C, p.L983F, or p.G993A) ATF7IP-JAK2 were incubated for 72 h with either a DMSO vehicle control or a dose response of type-I JAK inhibitors including rux, BMS-911543, AZD-1480, or fedratinib. The percentage of cell death was measured following a 20-min incubation with annexin-V and a live/dead cell stain, and then analysis by flow cytometry. Linear regression or non-linear regression models were fit to appropriate normalized data. Error bars indicate SEM over the mean of three biological replicates. c Table displaying LD50 concentrations (nM) for each cell line treated with JAK inhibitors shown in (b).