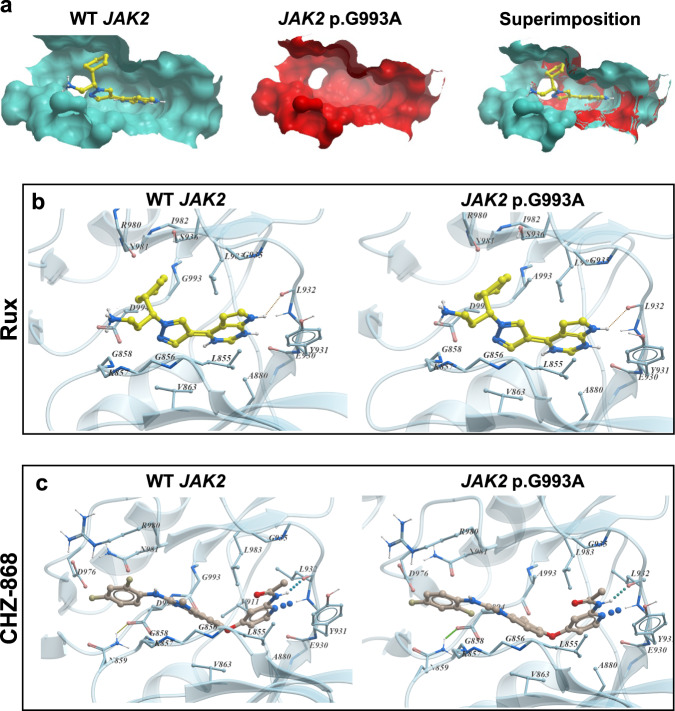
Fig. 5. The ability of the JAK2 p.G993A mutation to confer resistance to rux and CHZ-868 was not supported by computational modeling.
a JAK2 ATP-binding cavity volume changes due to the JAK2 p.G993A mutation. Receptors are depicted as surface representations with wild-type JAK2 receptor shown in cyan (left) and JAK2 p.G993A-mutant JAK2 receptor shown in red (middle). Superimposition of the wild-type JAK2 receptor with ligand (rux) cavity upon the JAK2 p.G993A-mutant JAK2 pocket (right). Docking of ligands rux (b) and CHZ-868 (c) to either WT JAK2 or JAK2 p.G993A kinase domains. Rux is colored with yellow carbon atoms and CHZ-868 is colored with light brown carbon atoms. Ligand docked to WT JAK2 (left) and ligand docked to JAK2 p.G993A-mutant JAK2 (right).