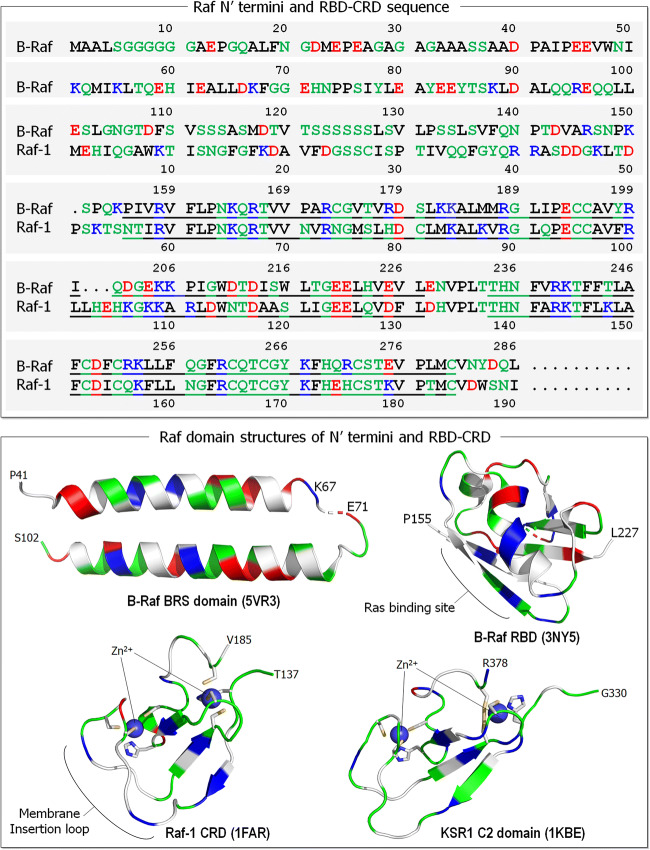
Fig. 4.
Sequences of the N′ termini and RBD-CRD of Raf isoforms, B-Raf and Raf-1 (upper panel). In the sequences, basic residues (positively charged) are colored in blue, acidic residues (negatively charged) are colored in red, hydrophobic residues are colored in black, and polar and glycine residues are colored in green. The B-Raf N′ terminus is longer (154 residues) than that of Raf-1 (54 residues). Underlines denote the RBD and CRD residues. A collection of domain structures for Raf N-terminal region are shown in the lower panel. Crystal structures of B-Raf-specific (BRS) domain (PDB: 5VR3) and B-Raf RBD (PDB: 3NY5). Solution structures of Raf-1 CRD (PDB: 1FAR) and kinase suppressor of Ras 1 (KSR1) C2 domain (PDB: 1KBE). In the cartoon, the same colors are used as in the sequence, except the hydrophobic residues colored in white. In Raf-1 CRD, sticks highlight the Cys152, Cys155, His173, and Cys176 residues coordinated with the first Zn2+, and the His139, Cys165, Cys168, and Cys184 residues coordinated with the second Zn2+. Similarly, for KSR1 C2 domain His334, Cys359, Cys362, and Cys377 coordinated with the first Zn2+, and Cys346, Cys349, His367, and Cys370 coordinated with the second Zn2+