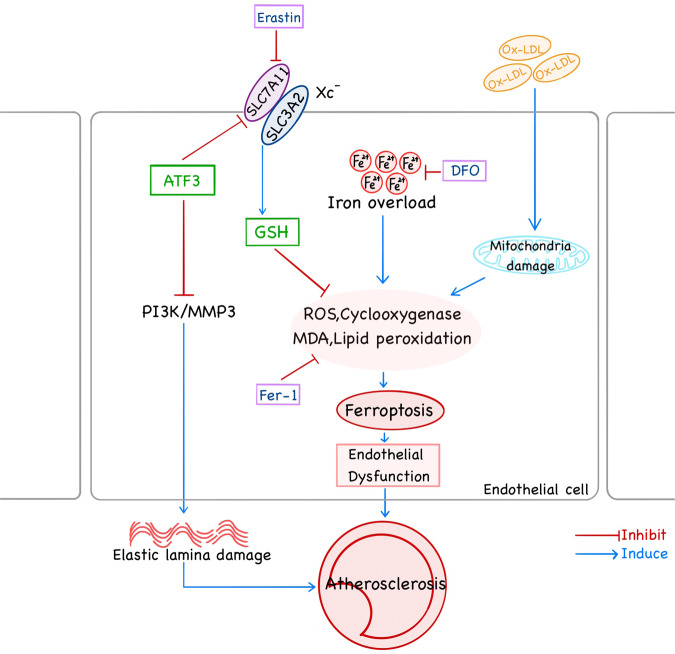
Fig. 2. Role of ferroptosis mutual effect of AS in endothelial cells.
The accumulation of lipid peroxides in endothelial cells that cause ferroptosis derived from two pathways. The extracellular ox-LDL causes endothelial cell mitochondrial damage, and intracellular iron overload causes lipid peroxide accumulation, which can be reserved by fer-1. Meanwhile, ATF3 inhibits its clearance pathway, and has a protective effect on atherosclerosis by reducing the damage of elastic membrane by inhibiting the PI3K-MMP3 pathway. The ferroptosis of endothelial cell and elastic lamina damage leads to endothelial dysfunction promoting the formation of AS.