FIGURE 4.
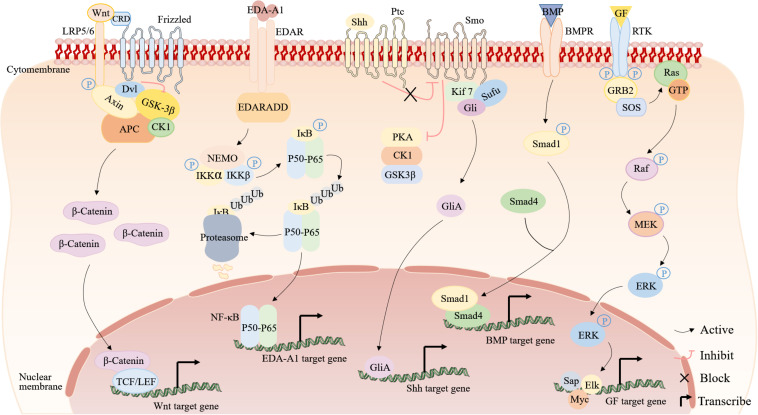
The signaling pathways involved in ESG development and regeneration. From left to right are the Wnt, EDA-A1, Shh, BMP, and ERK signaling pathways. Wnt signaling pathway (Nusse and Clevers, 2017; Routledge and Scholpp, 2019): in the absence of Wnt signals, GSK-3β/Axin/APC/β-catenin/CK1 is a destruction complex. GSK-3β phosphorylates β-catenin, thereby inhibiting its activity and then β-catenin is degraded by ubiquitination. When Wnt proteins bind to a receptor complex, it induces the association of Axin and Dvl with LRP5/6 and Frizzled. Dvl inhibits GSK-3β and the destruction complex falls apart, and thus prevents the degradation of β-catenin, permitting β-catenin accumulation, leading to binding TCF/LEF in the nucleus to upregulate target genes. EDA signaling pathway (Oeckinghaus et al., 2011; Sisto et al., 2016): in the absence of EDA-A1 signals, NF-κB dimers (P50–P65) are bound to inhibitory IκB proteins, which sequester inactive NF-κB complexes in the cytoplasm. When EDA-A1 binds to EDAR, stimulation of EDAR leads to the binding of EDARADD, for IKK activation. Shh signaling pathway (Fattahi et al., 2018; Xin et al., 2018): in the absence of Shh signals, Ptc inhibits the activity of Smo by affecting its localization to the cell surface, and protein kinases (PKA, CK1, and GSK3β) constitutively phosphorylate Gli proteins to inhibit the Gli. The secreted active Shh ligand binds to Ptc and relieves the repressive effect of the Ptc on Smo, activating the Smo, which then translocates to the cell membrane to inhibit PKA, CK1, and GSK3, providing an assembly platform for the recruitment of Kif7, Sufu and Gli, thus activating the Gli. Subsequently, the activated Gli forms (GliAs) translocate into the nucleus and activate Shh target genes. BMP signaling pathway (Gonzalez and Medici, 2014): when BMPs bind to BMPRs, intracellular Smad1 becomes phosphorylated. The phosphorylated Smad1 binds to Smad4 and then translocates into the nucleus and activates BMP target genes. ERK signaling pathway (Calvo et al., 2010; Gallo et al., 2019): Phosphorylated RTK binds to GRB2, and GRB2 binds to SOS, which stimulates RAS. RAS initiates activation of the MEK-ERK cascade by converting a molecule from GDP to GTP.