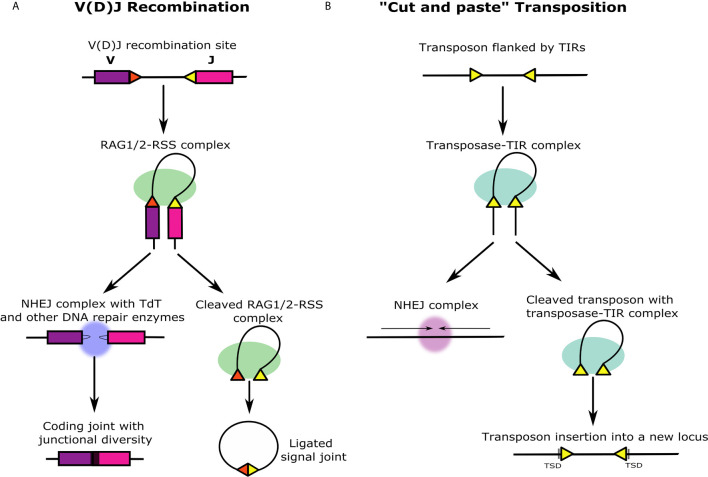
Figure 1.
Similarities and differences between V(D)J recombination and ‘cut and paste’ transposition. (A) V(D)J recombination occurs at the immune gene loci in differentiating lymphocytes during early T and B cell maturation stages. The RAG1/2 protein complex (green) binds to two asymmetric RSSs (yellow and red triangles) flanking V, D, and J gene segments (in this illustration, the D segment is not shown). The DNA double helix bends and folds into the recombination synaptic complex based on the selected RSS pair. Next, RAG1/2 introduces a nick at the intersection between each RSS and the coding gene segment that leads to the formation of closed DNA hairpins on the coding segments, and blunt, 5′ phosphorylated RSS ends at the signal ends that remain associated with the RAG1/2 complex and are ligated together forming a signal joint. The signal joint circle is deleted from the genome. Before ligation, the coding ends are subjected to further diversification by DNA repair enzymes together with TdT (blue) that generate junctional sequence diversity (black region between purple and pink gene segments). (B) ‘Cut and paste’ transposition starts similarly to V(D)J recombination with the transposase enzymes binding to the TIRs flanking the ends of the transposon (yellow triangles). Analogous to the beginning of the V(D)J recombination, the DNA double helix bends and folds into a transposition synaptic complex. The transposase makes double-stranded breaks in the DNA, and the transposon is entirely excised including the TIRs. The genomic location from which the transposon is excised is immediately ligated by NHEJ mechanism. Unlike the excised V(D)J signal joint circle that is lost from the genome, the excised transposon with the transposase-TIR complex creates a double-stranded break in a different region in the genome and integrates into the target site. This activity generates target site duplications (TSDs) on both sides of the integrated transposon that are formed similarly in RAG transposition events.