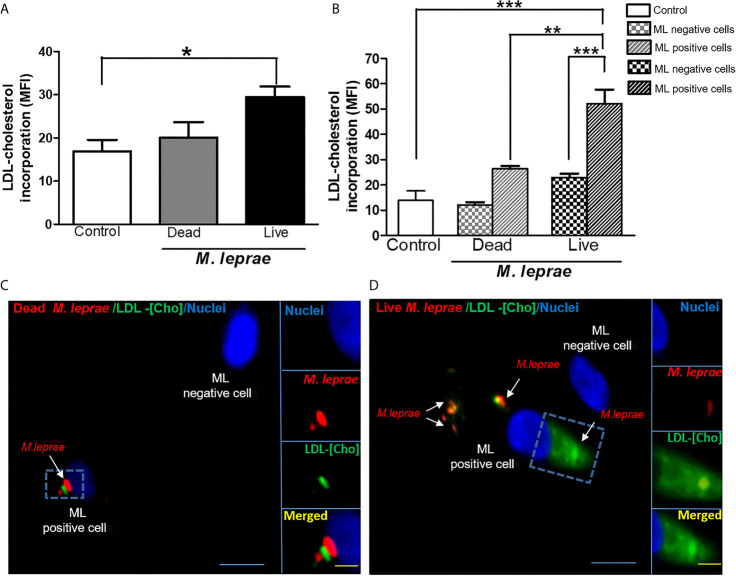
Figure 1.
M. leprae-infected human SCs display increased uptake of LDL-cholesterol. ST88-14 human SC line was incubated with PKH26-labeled (red) M. leprae (ML) at a MOI of 50:1 for 48 h, followed by 2 h incubation with LDL-[Cho] (green). (A, B) LDL-[Cho] incorporation and bacterial association was measured simultaneously by flow cytometry and is expressed as medium fluorescence intensity (MFI). Results from three representative experiments are shown. Statistically significant differences (*p < 0.05 by Student’s t-test statistical analyses) (** p< 0.01 and ***p < 0.0001 - ANOVA test followed by Bonferroni as a post-test were performed and used for statistical analyses). (C, D) Confocal microscopy images showing LDL-cholesterol (green) incorporation in stimulated and infected cells. Dead and live M. leprae are labeled in red with PKH26 and nuclei are labeled in blue with DAPI. Arrows indicate colocalization of LDL-[Cho] with M. leprae. Scale bar, 5µm (blue) and 10µm (yellow).