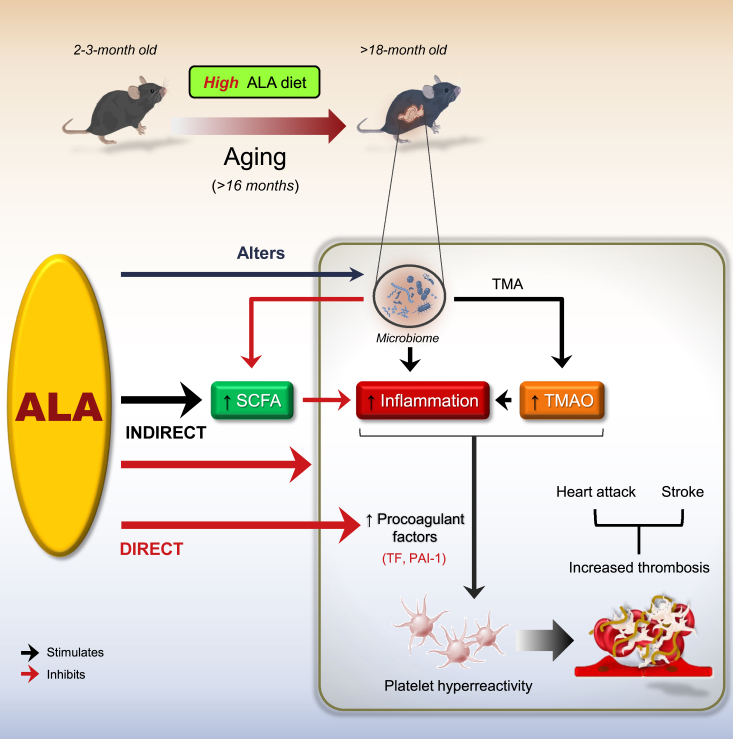
Figure 6.
Schematic illustrating the benefits of lifelong dietary ALA for the suppression of age-associated atherothrombotic events
The scheme illustrates a metaorganismal pathway showing that lifelong nutritional supplementation with ALA attenuates platelet hyperresponsiveness and enhanced thrombotic risk both directly through the reduction of procoagulant factors and indirectly through the modulation of the gut microbiota and its metabolites TMAO and SCFA acetate, as well as the suppression of inflammatory responses in aged mice. ALA, ɑ-linolenic acid; SCFA, short-chain fatty acid; TMA, trimethylamine; TMAO, trimethylamine N-oxide. Black arrow indicates stimulation; Red arrow indicates inhibition.
See text for details.