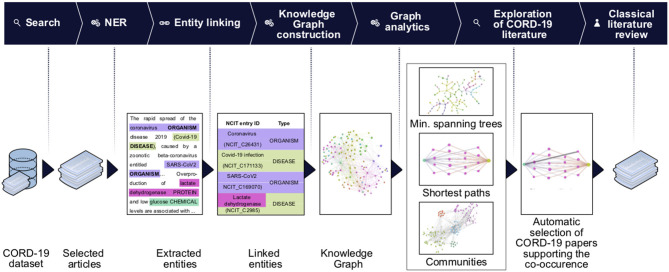
Figure 1.
Knowledge graph construction and analysis pipeline. Entities of interest are extracted using the named entities recognition (NER) techniques on the entire CORD-19 dataset, or on a subset of articles selected for matching user-specified query (Search). The extracted entities are then linked to the NCIT ontology terms and passed to the knowledge graph construction stage. On this stage we build a knowledge graph using extracted and linked terms as nodes and their co-occurrences as edges. The association strength between terms is quantified using a mutual-information based score of their co-occurrences. We perform various graph analytics tasks (e.g., community detection, BMIPs, minimum spanning trees computation) that allow us to navigate the knowledge graph and reveal connectivity patterns and subgraphs carrying the most important terms and their co-occurrences. Data from the graphs are then used to guide further literature review: a first seed set of article was obtained from the CORD-19, examining the articles featuring co-occurrence of terms of interest (first automatic selection of CORD-19 articles). Guided by this set of articles, we then perform a second step of classical literature review and consider other sources, not included in CORD-19 (see detailed description of the steps in section Methods).