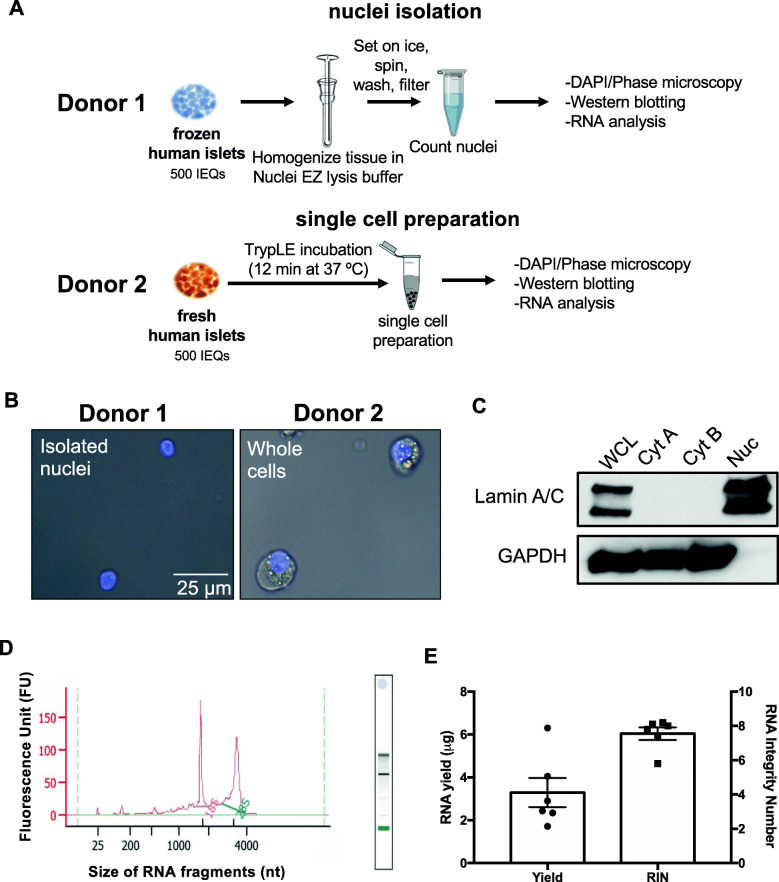
Fig. 1.
Single nuclei isolation from frozen human islet samples. A Experimental workflow of isolation of nuclei from frozen cultured human islets (donor 1) and human islet dispersion into single cells (donor 2). B Isolated nuclei from frozen human islets (donor 1) and dissociated human islet cells from fresh intact islets (donor 2, whole cells) were imaged by DAPI/Phase microscopy. Left image: Intact nuclei stained in blue without cytoplasm surrounding the isolated nucleus . Right image: Nuclei stained in blue surrounded by cytoplasm of human islet cells. Scale bar is 25 μm. C Western blot analysis of human pancreatic islet cells (whole cell lysate; WCL, obtained from donor 2), supernatant collected after the first centrifuge step (cytosolic fraction A; Cyt A) and second centrifuge step (cytosolic fraction B; Cyt B) of the nuclear isolation protocol, and isolated nuclei (nuclear fraction; Nuc, obtained from Donor 1). LaminA/C is a nuclear marker; GAPDH is a cytoplasmic marker. D RNA was isolated from islet cell nuclei and analyzed by Bioanalyzer. Representative electropherogram showing two major peaks (18S and 28S rRNA) indicates minimal degradation of total RNA. The X-axis indicates the size of RNA fragments (nt: nucleotides) and the Y-axis represents the intensity of the fluorescence signal (FU, fluorescence unit). E Yield (μg, left Y-axis, dots) and RNA Integrity Number (RIN, right Y-axis, squares) of RNA isolated from six technical replicates across three independent experiments. Data are represented as mean ± SEM