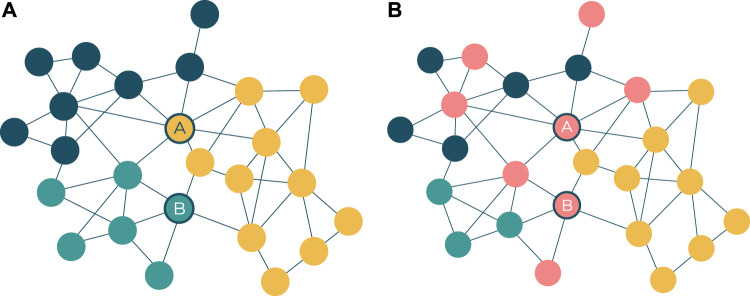
FIGURE 2.
(A) Pivotal proteins (represented by nodes A and B) are loosely defined as proteins that facilitate cross-talk between network modules. This has some overlap with the notion of a node with high betweenness centrality (Freeman 1977), but there is emphasis on the node’s connectivity across network modules. Node A represents a target belonging to the yellow network module and interacts with the highest number of targets in the blue module. Node B represents a target belonging to the green network module and interacts with the highest number of targets in the yellow module. (B) Pathway membership, represented by nodes colored red, can be scattered across different network modules. While the modules in the network may represent distinct GO processes, biological pathways serve multiple such processes and are therefore seldom confined to one module.