Figure 1.
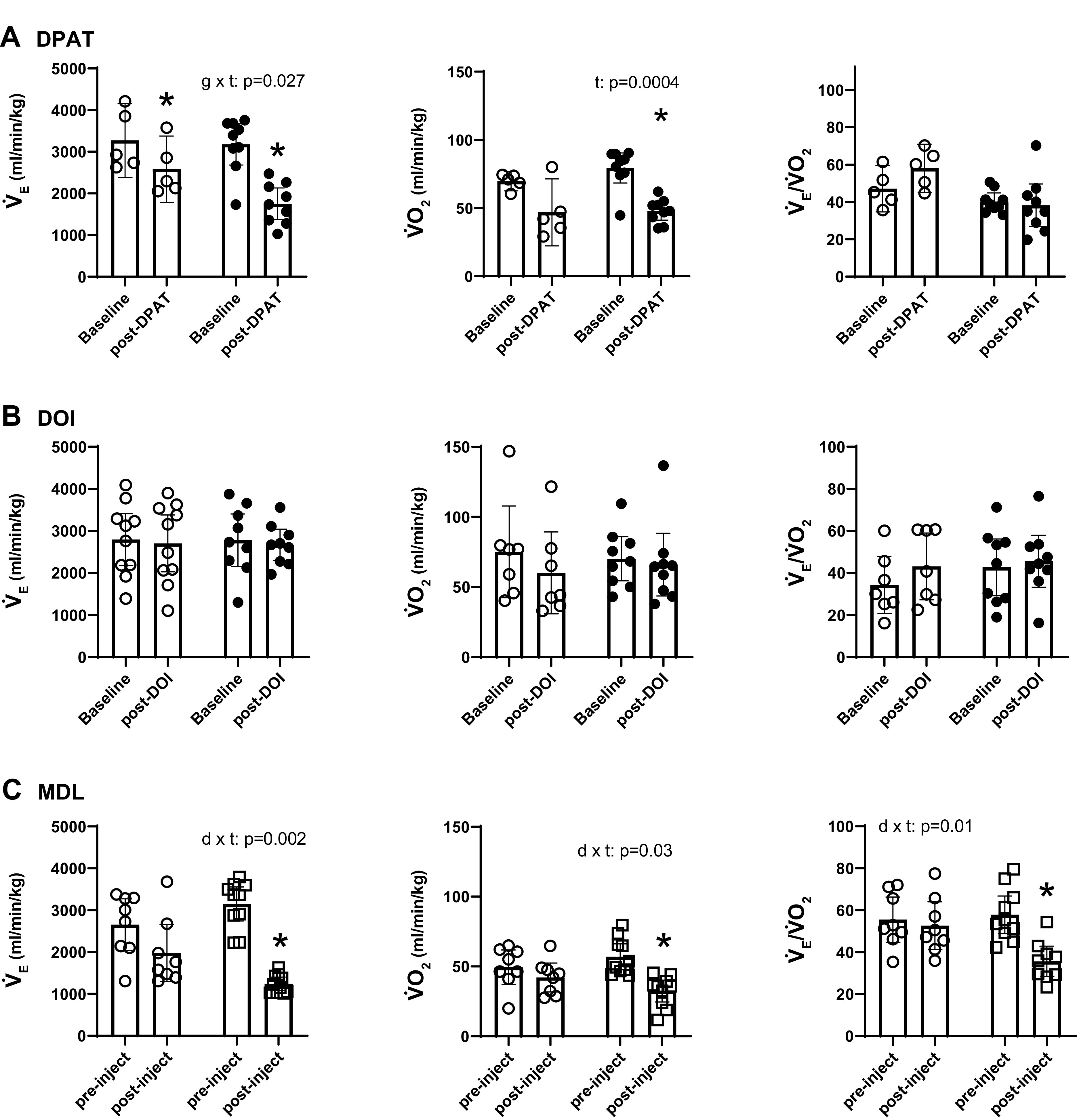
Effects of 8-OH-DPAT (A) and DOI (B) on ventilation (V̇e), metabolic oxygen consumption (V̇o2), and the ventilatory equivalent (V̇e/V̇o2) of TPH2+/+ (open circles, n = 5) and TPH2−/− littermates (closed circles; n = 9) under baseline, resting conditions. C: effects of vehicle (DMSO; open circles; n = 8) or MDL-11,939 (MDL, open squares; n = 10) on these variables in TPH2+/+ mice. Significant effects of genotype (g) (in A and B) or drug (d) (in C) and time (t) assessed with a two-way repeated measures ANOVA, with Tukey’s post hoc tests. *Significant effect of drug (post hoc: P < 0.05). DOI, 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine; DPAT, 8-OH-DPAT; TPH2, tryptophan hydroxylase 2; TPH2+/+ mice, wild-type mice; 8-OH-DPAT, 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin.
