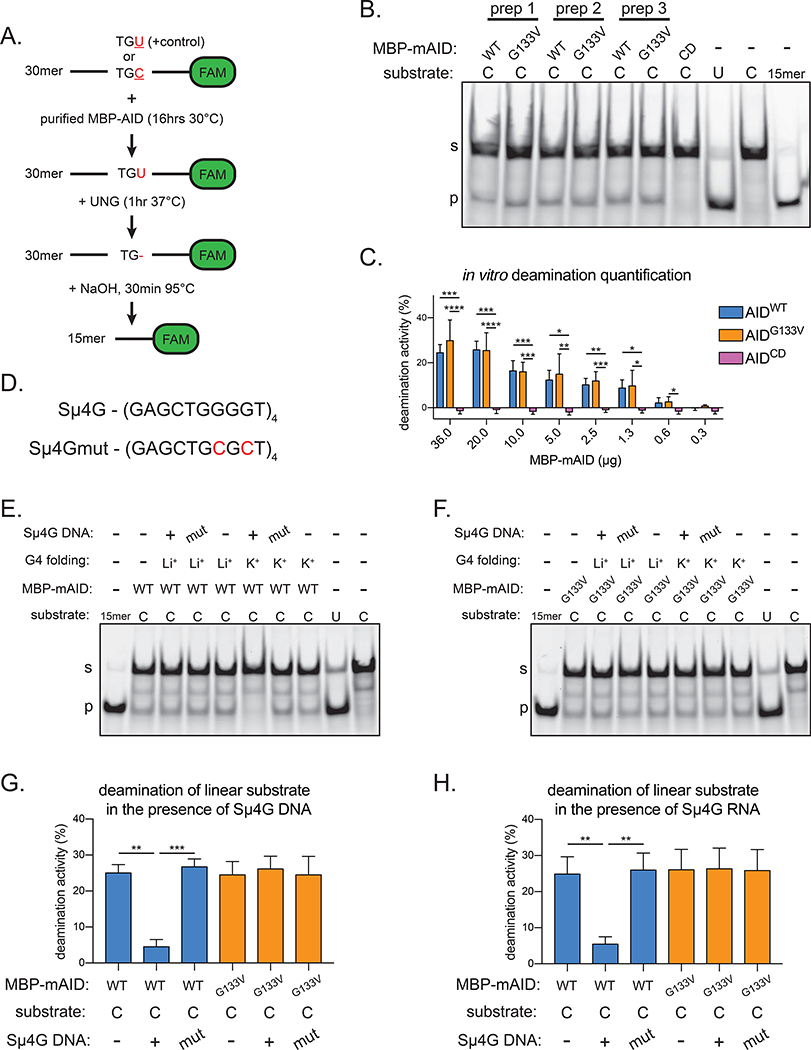
Figure 4. AIDG133V retains DNA deamination activity.
(A) Schematic of AID in vitro deamination assay. FAM, 6-carboxyfluorescein. TGU, positive control representing 100% cytidine deamination; TGC, AID deamination substrate. (B) Representative TBE-Urea gel showing the products of in vitro deamination reactions with purified MBP-mouse AID (MBP-mAID) proteins, quantified in Figure S5A. Purified MBP-mAID proteins shown in Figure S4F–J. CD, catalytically dead AIDH56R/E58Q. (C) Quantification of deamination assays with varying amounts of purified MBP-mAID proteins, representative gels shown in Figure S5E. (D) G4 substrate derived from Igh-Sμ locus (Sμ4G) and mutant sequence unable to form G4 (Sμ4Gmut). Substrate characterization in Figure S5F. (E,F) Representative TBE-Urea gels showing the products of in vitro deamination reactions with purified mouse MBP-mAID proteins, performed with or without G4 DNA or RNA, quantified in (G,H). Mut, Sμ4Gmut; Li+, G4 folded in presence of Li+ (destabilizes G4s); K+, G4 folded in presence of K+ (stabilizes G4s). Data in (B) are representative of 2 independent experiments, (C, E-H) are from, or representative of, 4 or 5 independent experiments using 2 (C) or 3 (E-H) independent protein preparations. (B, E-F) “s” denotes substrate, “p” denotes product. Error bars represent the mean ± std. dev. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; p-values calculated using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test with (G,H) or without (C) pairing.