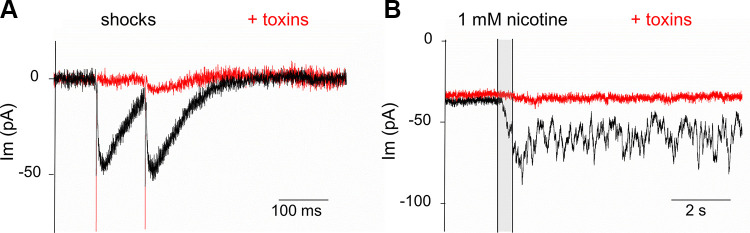
Fig. 5.
Voltage-gated calcium channels and nicotine. A: a cocktail of voltage-gated calcium channel antagonists (400 nM ω-agatoxin IVA, 1 µM ω-conotoxin GVIA, and 500 nM SNX-482) blocked shock-evoked postsynaptic currents. Shock artifacts precede the postsynaptic currents (inward at the holding potential of −94 mV). B: the same cocktail of antagonists reduced nicotine-evoked transient membrane currents. Toxin block required long application time (>15 min). Nicotine (1 mM) was applied during time of shaded vertical bar.