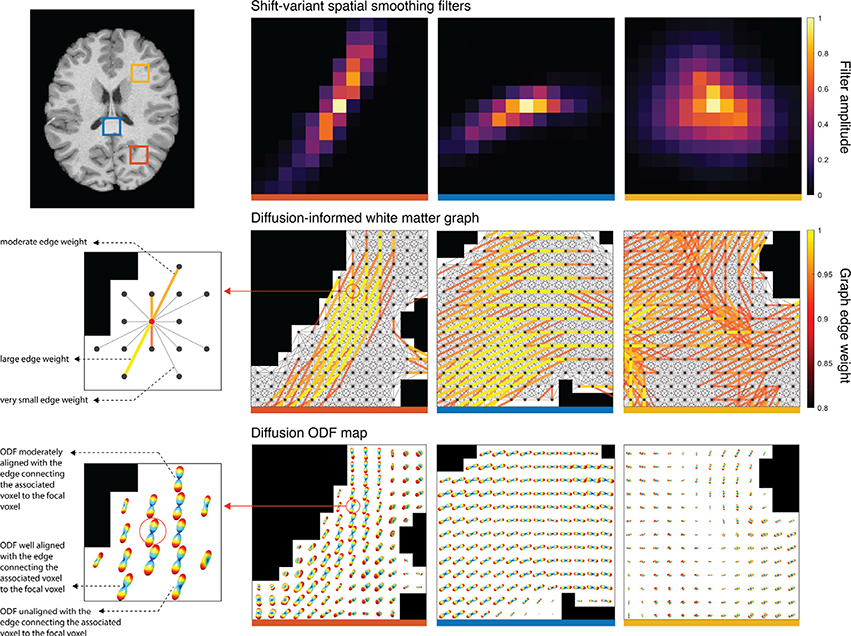
Fig. 5.
Generation of diffusion-informed smoothing filters. Diffusion ODFs (bottom row) serve as the basis for the creation of a WM graph (middle row). Every WM voxel corresponds to a vertex in the graph, with weighted connections to neighboring voxels (middle left). The edge weights are determined on the basis of coherence between the directions of diffusion and the orientation of the graph edges (bottom left). Using this WM graph definition, graph filters from a single spectral profile become adaptive to the local axonal microstructure when instantiated in different WM regions (top row). Note that both the edges connecting voxels and the graph filters extend in three dimensions, whereas their 2D axial intersection centered at the focal voxel are shown. Graph parameters: 5-conn neighborhood, α = 0.9, β = 50; filter parameters: τ = 7. Filters are shown normalized to the [0,1] range. ODF interpolation and visualization were performed using the public CSA-ODF package4.