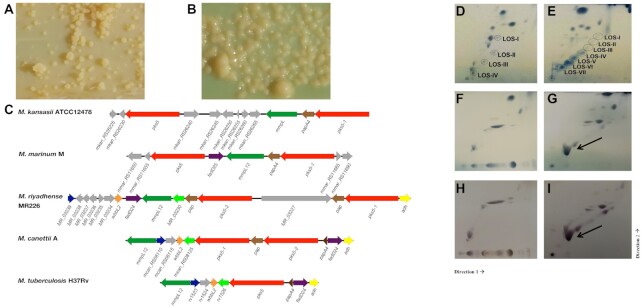
Figure 4.
pks5 loci in M. riyadhense and other related mycobacteria and 2D-TLC analysis of polar lipids extracted from selected M. riyadhense strains, M. kansasii (subtype I), M. marinum M, M. smegmatis MC-1551. (A) Rough-dry colony morphology (MR193) and (B) smooth morphology (MR226) of M. riyadhense. (C) Genetic locus map of the pks5 gene cluster from M. riyadhense MR226, M. marinum M (partial), and M. kansasii ATCC12478 (partial), M. canettii A and M. tuberculosis H37Rv (drawn to scale). The arrows show the direction of transcription and the genes are coloured according to the orthologous relationships. Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv does not produce LOSs and the pks5 loci was drawn for genomic comparison purpose. Polar lipids from two known LOS producers, M. marinum (D) and M. kansasii (E), are included to illustrate the migration pattern of LOS species in System E. (F) 2D-TLC analysis of polar lipids extracted from select M. riyadhense rough strain or smooth (G) strain. A separate staining with alpha-napthol also confirmed that this was a glycolipid species from the same (H) rough and (I) smooth strain. (D–G) were charred after staining with MPA, while (H) and (I) were charred after staining with alpha napthol. LOS III from M. riyadhense is indicated by a solid arrow.