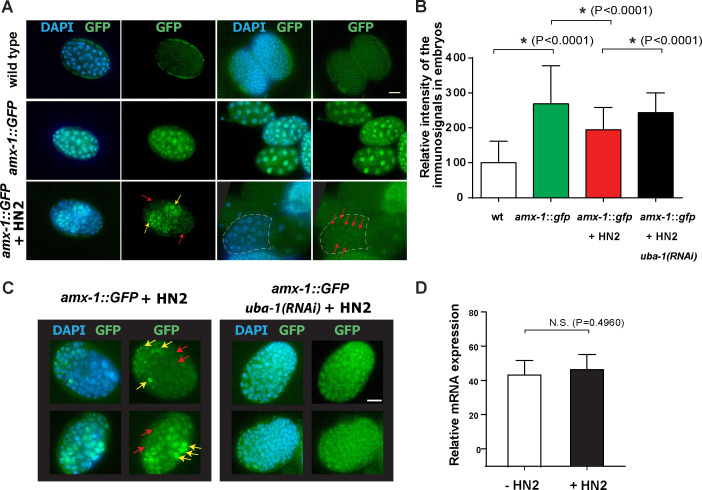
Fig 6. Interstrand crosslink DNA damage leads to ubiquitination-dependent AMX-1 relocalization.
(A) Nitrogen mustard (HN2) exposure induces relocalization of AMX-1::GFP signals. Arrows indicate embryo cells containing no/weak (red) or stronger (yellow) signals. Bar,10μm. (B) Quantitation of relative intensity of the AMX-1::GFP signal in embryos from the indicated genotypes. Asterisks indicate statistical significance. 66–250 embryos from 6–8 worms were analyzed. Error bars represent standard deviations. (C) Depletion by RNAi of the E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme UBA-1, suppresses the uneven/mosaic signals exhibited in amx-1::GFP transgenic animals. AMX-1::GFP signal intensity from embryos are quantitated in panel B. P = 0.1084 from amx-1::GFP + HN2. (D) mRNA expression level of amx-1 is not altered after HN2 treatment. P = 0.4960. Error bars represent standard deviations.