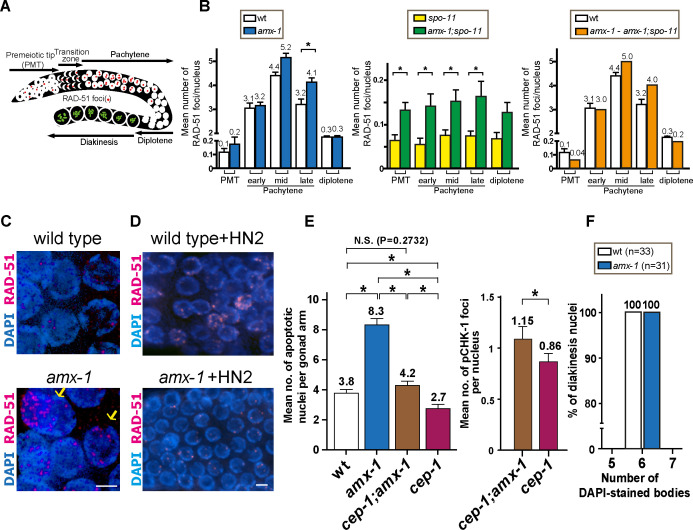
Fig 7. AMX-1 is required for DNA repair and lack of AMX-1 activates cep-1/p53-dependent germ cell apoptosis.
(A) Diagram of a C. elegans germline indicating the germline nuclei progression and the position of zones scored for RAD-51 foci. Image is modified from Kim et al [22]. (B) Histogram represents the quantitation of RAD-51 foci in germlines of the indicated genotypes. Shown are the mean numbers of RAD-51 foci observed per nucleus on each zone along the germline axis (x-axis). We compared the levels of RAD-51 foci between wild type and amx-1 mutants (left) and monitored SPO-11-independent (middle) and SPO-11-dependent (right panel) RAD-51 foci levels. To identify the levels of SPO-11-dependent (meiotic) foci, the mean number of RAD-51 foci observed in amx-1;spo-11 mutants was subtracted from those in amx-1 mutants. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. Asterisks indicate statistical significance by the two-tailed Mann–Whitney test, 95% C.I. (C) amx-1 mutants contain pachytene nuclei with >10 RAD-51 foci per nucleus which may undergo apoptosis (indicated by yellow arrows, 10 out of 25 gonads). Bar, 2 μm. (D) High-resolution images of pachytene nuclei from wild type and amx-1 mutants with 150 μM HN2 treatment immunostained for RAD-51. Bar, 2 μm. (E) Left, quantification of germline apoptosis in the indicated genotypes. cep-1/p53 is a mutant with defective DNA damage-induced apoptosis utilized as a control. Asterisks indicate statistical significance. P = 0.2732 for wt and cep-1;amx-1. P < 0.0001 all others, by the two-tailed Mann–Whitney test, 95% C.I. Right, Quantification of pCHK-1 foci in pachytene nuclei in the indicated genotypes. P = 0.0299 for cep-1;amx-1 and cep-1 by the t-test, 95% C.I. (F) Number of DAPI-stained bodies observed in diakinesis oocytes from the indicated genotypes. The number of -1 oocytes scored (n) is indicated next to the genotypes.