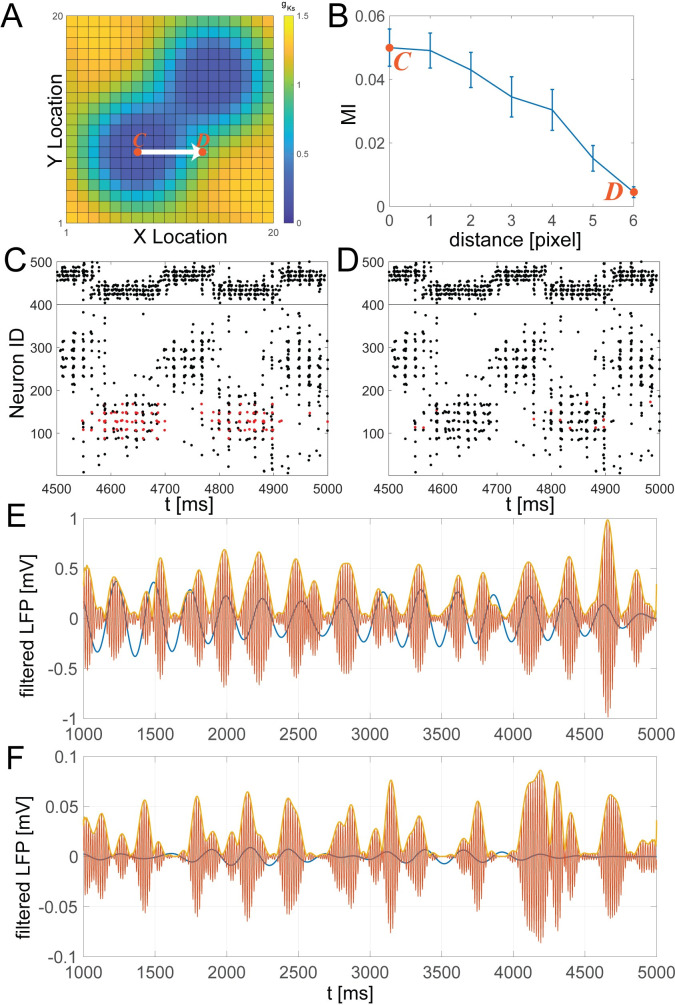
Fig 6. Strength of theta-gamma coupling as a function of the distance from the low gKs region.
A local field potential (LFP) signal was constructed from spike trains of E cells at different distances from the center of a gKs hotspot. A, Double peaked gKs spatial mapping with locations marked to calculate LFPs. B, Modulation Index (MI) between gamma and theta filtered LFP traces as a function of the distance from the center of the gKs hotspot (as indicated in A.) C and D, Example raster plot of the network-wide spiking near the hotspot (C, as marked on A) and away from the hotspot (D, as marked on A). E cells are numbered 1 to 400, and I cells are numbered 401 to 500. Cells used to compute the LFP signal are marked in red. E and F, Examples of theta (blue curve) and gamma (orange curve) filtered LFP signals computed at locations near (C) and far (D) from the hotspot, marked on A, B.