Fig. 3. Magnetic tweezers showing PARP1-induced condensation on undamaged DNA.
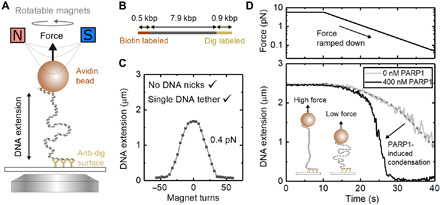
(A) Schematic of magnetic tweezers showing DNA stretched between the bead and coverslip. The height of the magnets controls the force acting on the bead, and the bead can be rotated by rotating the magnets. (B) DNA construct used for magnetic tweezers with two labeled handles acting as attachment points. (C) Single DNA tethers without nicks are selected by examining the characteristic response of DNA extension to magnet turns. (D) Effect of force ramp on DNA extension in the presence of 400 and 0 nM PARP1. At low forces (<1 pN), PARP1 induces significant compaction of the DNA. The dashed gray line shows a fit of the worm-like chain model to the DNA extension for 0 nM PARP1 with a fixed persistence length of 50 nm. The DNA contour length was a free parameter for the fit and yielded 2.7 μm in good agreement with the expected length of 2.6 μm for the 7.9-kbp DNA.
