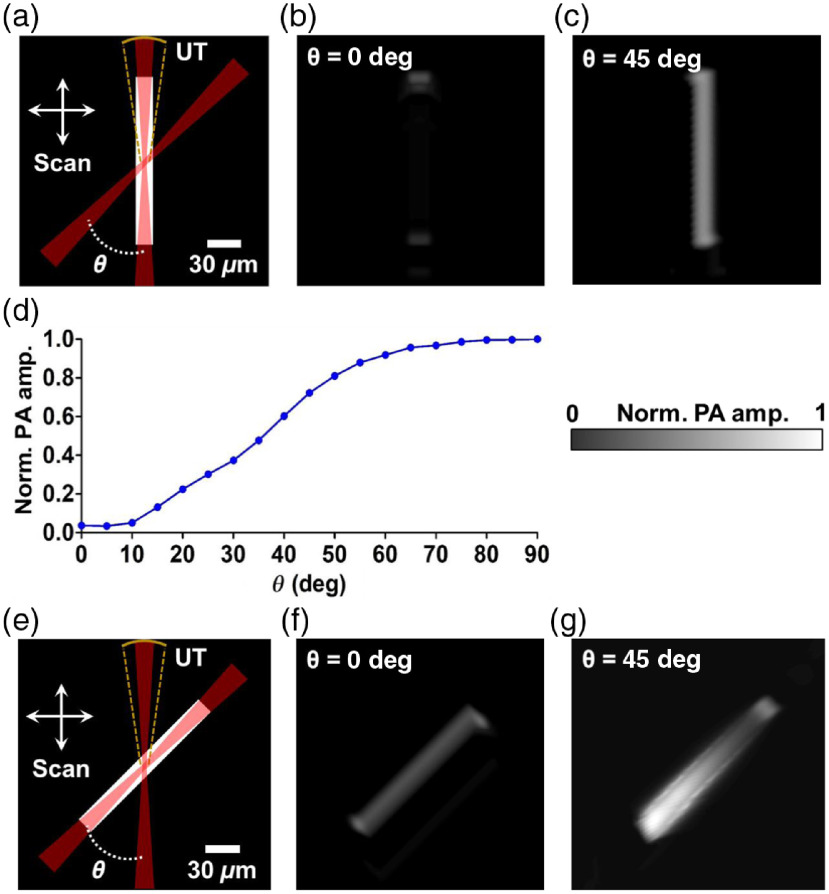
Fig. 1.
Numerical simulation of the virtually augmented view angle of DAI-PAM. (a) Schematics of the simulation for the vertical phantom, which was imaged, respectively, with two Gaussian beams, one from the top, and the other from the upper right at an inclined angle (both with an ). The PA signals were detected by a focused ultrasonic transducer (UT) with an and a central frequency of 50 MHz. Two-dimensional scanning was applied to form an image. (b)–(c) The images formed by raster-scanning the phantom with the top and oblique illumination, respectively. The entire vertical feature was missed in (b). (d) The dependence of the received PA waves on the inclined angle. (e) Schematics of the simulation for the 45-deg oblique phantom. (f)–(g) The images formed by raster-scanning the phantom with the top and oblique illumination at , respectively. The phantom absorber could be reconstructed with both the top and oblique illumination.