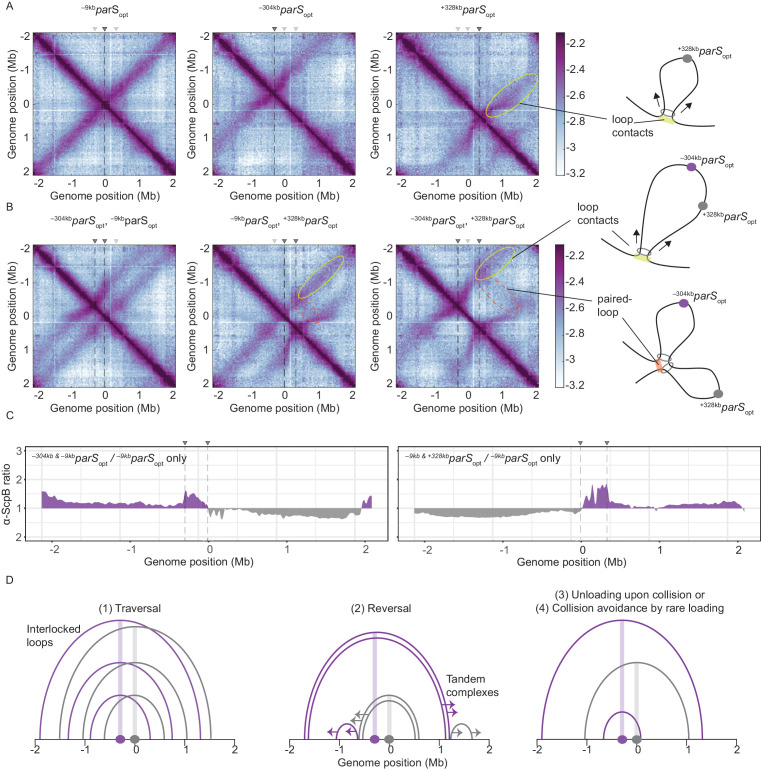
Figure 3. Overlapping chromosome arm alignment patterns for wild-type Smc.
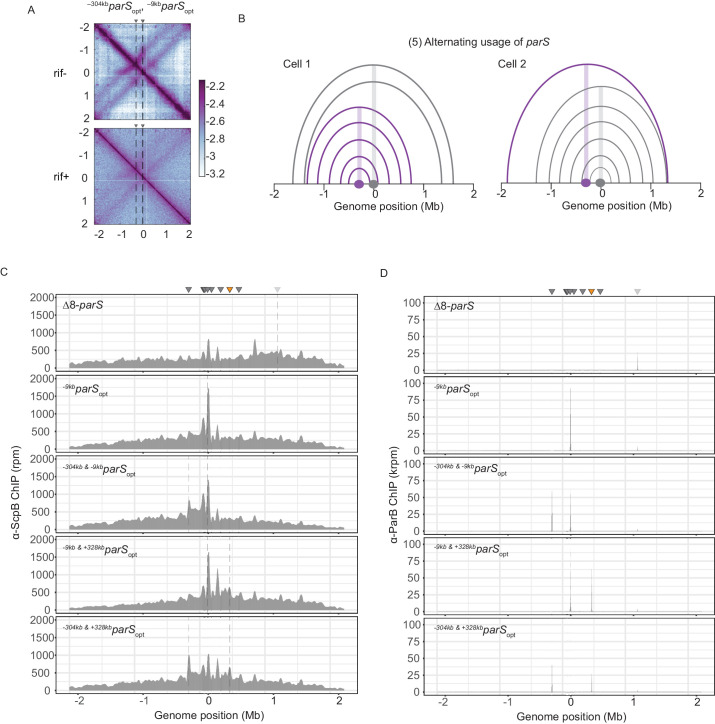
(A) Normalized 3C-seq contact maps for strains with a single parSopt site at −9 kb, −304 kb, or +328 kb. Dark gray triangles above the contact maps indicate the presence of active parS sites. Light gray triangles for reference are parS sites absent in the given experiment. Schemes depict a ‘loop contact’ that emerges by bidirectional translocation of a Smc unit from a single loading site (yellow), here +328kbparSopt. (B) Normalized 3C-seq contact maps for strains with two parSopt sites spaced by ~300 kb (left and middle) or ~600 kb (right). Schemes interpreting interactions in the contact maps: loop contacts (in yellow colors) and ‘paired-loop contacts’ that we presume to emerge by collision of two convergently translocating Smc units loaded at opposite parS sites (in orange colors). (C) Ratio plots for ChIP-seq read counts for a strain with two parS sites (left panel: –304kbparSopt and –9kbparSopt; right panel: –9kbparSopt and +328kbparSopt) and a control strain with a single parS site (–9kbparSopt). Representation as in Figure 2B. (D) Schemes depicting possible scenarios for long-distance contacts emerging by bidirectional Smc translocation with collision avoidance and collision resolution: Smc traversal (1), reversal (2), unloading upon collision (3), or low Smc flux (4).